Computational and structural biology

Spider-like proteins spin defenses to control immunity
Researchers from Utrecht University discovered two distinct binding modes of a spider-shaped immune inhibitor found in serum.
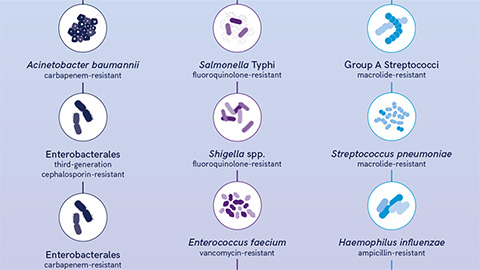
Training AI to uncover novel antimicrobials
Antibiotic resistance kills millions, but César de la Fuente’s lab is fighting back. By pairing AI with human insight, researchers are uncovering hidden antimicrobial peptides across the tree of life with a 93% success rate against deadly pathogens.
AI-designed biomarker improves malaria diagnostics
Researchers from the University of Melbourne engineered Plasmodium vivax diagnostic protein with enhanced yield and stability while preserving antibody-binding, paving the way for more reliable malaria testing.
Antibiotic sensor directly binds drug in resistant bacteria
Researchers at Drexel University uncover how the vancomycin-resistant bacterial sensor binds to the antibiotic, offering insights to guide inhibitor design that restores antibiotic effectiveness against hospital-acquired infections.
AI unlocks the hidden grammar of gene regulation
Using fruit flies and artificial intelligence, Julia Zeitlinger’s lab is decoding genome patterns — revealing how transcription factors and nucleosomes control gene expression, pushing biology toward faster, more precise discoveries.
How sugars shape Marfan syndrome
Research from the University of Georgia shows that Marfan syndrome–associated fibrillin-1 mutations disrupt O glycosylation, revealing unexpected changes that may alter the protein's function in the extracellular matrix.
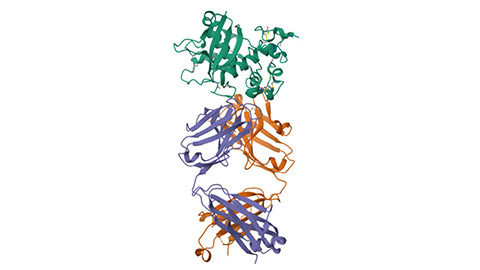
Glow-based assay sheds light on disease-causing mutations
University of Michigan researchers create a way to screen protein structure changes caused by mutations that may lead to new rare disease therapeutics.

Understanding the lipid link to gene expression in the nucleus
Ray Blind, an ASBMB Breakthroughs speaker, presented his research on how lipids and sugars in the cell nucleus are involved in signaling and gene expression and how these pathways could be targeted to identify therapeutics for diseases like cancer.

Pathogen-derived enzyme engineered for antibiotic design
Engineered variants of a bacterial enzyme developed at the University at Buffalo accept larger substrates, paving the way for new acinetobactin-based antimicrobials. Read more about this recent JBC paper.
