Cell biology
A biological camera: How AI is transforming retinal imaging
AI is helping clinicians see a more detailed view into the eye, allowing them to detect diabetic retinopathy earlier and expand access through tele-ophthalmology. These advances could help millions see a clearer future.
Training AI to uncover novel antimicrobials
Antibiotic resistance kills millions, but César de la Fuente’s lab is fighting back. By pairing AI with human insight, researchers are uncovering hidden antimicrobial peptides across the tree of life with a 93% success rate against deadly pathogens.
AI-designed biomarker improves malaria diagnostics
Researchers from the University of Melbourne engineered Plasmodium vivax diagnostic protein with enhanced yield and stability while preserving antibody-binding, paving the way for more reliable malaria testing.
Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor reduces cancer invasion
Scientists at the Mayo Clinic engineered a TIMP-1 protein variant that selectively inhibits MMP-9 and reduces invasion of triple-negative breast cancer cells, offering a promising tool for targeted cancer research.
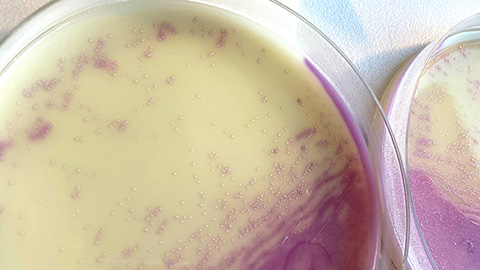
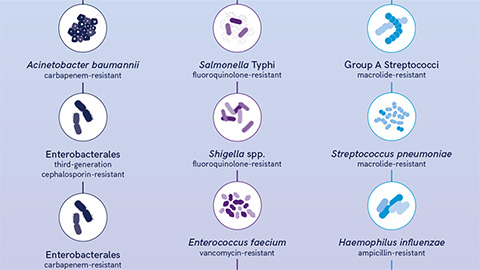
Antibiotic sensor directly binds drug in resistant bacteria
Researchers at Drexel University uncover how the vancomycin-resistant bacterial sensor binds to the antibiotic, offering insights to guide inhibitor design that restores antibiotic effectiveness against hospital-acquired infections.
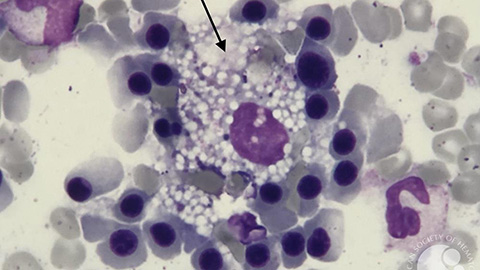
ApoA1 reduce atherosclerotic plaques via cell death pathway
Researchers show that ApoA1, a key HDL protein, helps reduce plaque and necrotic core formation in atherosclerosis by modulating Bim-driven macrophage death. The findings reveal new insights into how ApoA1 protects against heart disease.

Omega-3 lowers inflammation, blood pressure in obese adults
A randomized study shows omega-3 supplements reduce proinflammatory chemokines and lower blood pressure in obese adults, furthering the understanding of how to modulate cardiovascular disease risk.
AI unlocks the hidden grammar of gene regulation
Using fruit flies and artificial intelligence, Julia Zeitlinger’s lab is decoding genome patterns — revealing how transcription factors and nucleosomes control gene expression, pushing biology toward faster, more precise discoveries.
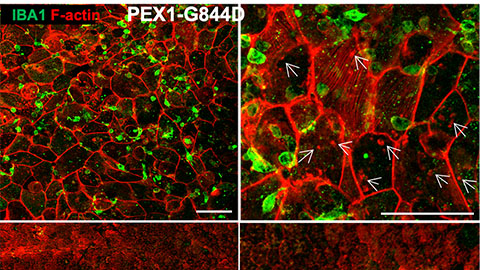
Early lipid changes drive retinal degeneration in Zellweger spectrum disorder
Lipid profiling in a rare disease mouse model reveals metabolic shifts and inflammation in the retinal pigment epithelium — offering promising biomarker leads to combat blindness.
