UCLA researchers engineer experimental drug for preventing heart failure after heart attacks
Scientists at the Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cell Research at UCLA have developed a first-of-its-kind experimental therapy that has the potential to enhance heart repair following a heart attack, preventing the onset of heart failure.
Cardiovascular disease continues to be the world’s leading cause of death, contributing to one-third of deaths annually. After a heart attack, the heart’s innate ability to regenerate is limited, causing the muscle to develop scars to maintain its structural integrity. This inflexible scar tissue, however, interferes with the heart’s ability to pump blood, leading to heart failure in many patients — 50% of whom do not survive beyond five years. The need for innovative therapies is urgent.
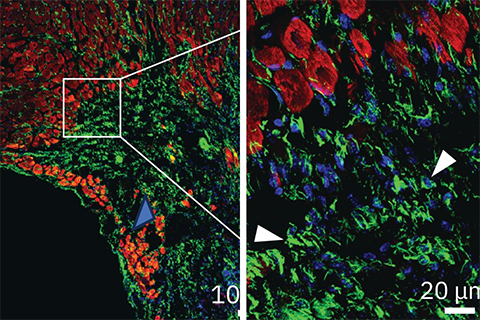
The new therapeutic approach aims to improve heart function after a heart attack by blocking a protein called ENPP1, which is responsible for increasing the inflammation and scar tissue formation that exacerbate heart damage. The findings, published in Cell Reports Medicine, could represent a major advance in post-heart attack treatment.
The research was led by senior author Arjun Deb, a professor of medicine and molecular, cell and developmental biology at UCLA.
“Despite the prevalence of heart attacks, therapeutic options have stagnated over the last few decades,” said Deb, who is also a member of the UCLA Broad Stem Cell Research Center. “There are currently no medications specifically designed to make the heart heal or repair better after a heart attack.”
The experimental therapy uses a therapeutic monoclonal antibody engineered by Deb and his team. This targeted drug therapy is designed to mimic human antibodies and inhibit the activity of ENPP1, which Deb had previously established increases in the aftermath of a heart attack.
The researchers found that a single dose of the antibody significantly enhanced heart repair in mice, preventing extensive tissue damage, reducing scar tissue formation and improving cardiac function. Four weeks after a simulated heart attack, only 5% of animals that received the antibody developed severe heart failure, compared with 52% of animals in the control group.
This therapeutic approach could become the first to directly enhance tissue repair in the heart following a heart attack; an advantage over current therapies that focus on preventing further damage but not actively promoting healing. This can be attributed to the way the antibody is designed to target cellular cross-talk, benefitting multiple cell types in the heart, including heart muscle cells, the endothelial cells that form blood vessels, and fibroblasts, which contribute to scar formation.
Initial findings from preclinical studies also show that the antibody therapy safely decreased scar tissue formation without increasing the risk of heart rupture — a common concern after a heart attack. However, Deb acknowledges that more work is needed to understand potential long-term effects of inhibiting ENPP1, including potential adverse effects on bone mass or bone calcification.
Deb’s team is now preparing to move this therapy into clinical trials. The team plans to submit an investigational new drug, or IND, application to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration this winter with the goal of beginning first-in-human studies in early 2025. These studies will be designed to administer a single dose of the drug in eligible individuals soon after a heart attack, helping the heart repair itself in the critical initial days after the cardiac event.
While the current focus is on heart repair after heart attacks, Deb’s team is also exploring the potential for this therapy to aid in the repair of other vital organs.
“The mechanisms of tissue repair are broadly conserved across organs, so we are examining how this therapeutic might help in other instances of tissue injury,” said Deb, who is also the director of the UCLA Cardiovascular Research Theme at the David Geffen School of Medicine. “Based on its effect on heart repair, this could represent a new class of tissue repair-enhancing drugs.”
This article is republished from the UCLA Newsroom. Read the original here.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
CRISPR epigenome editor offers potential gene therapies
Scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, created a system to modify the methylation patterns in neurons. They presented their findings at ASBMB 2025.

Finding a symphony among complex molecules
MOSAIC scholar Stanna Dorn uses total synthesis to recreate rare bacterial natural products with potential therapeutic applications.

E-cigarettes drive irreversible lung damage via free radicals
E-cigarettes are often thought to be safer because they lack many of the carcinogens found in tobacco cigarettes. However, scientists recently found that exposure to e-cigarette vapor can cause severe, irreversible lung damage.

Using DNA barcodes to capture local biodiversity
Undergraduate at the University of California, Santa Barbara, leads citizen science initiative to engage the public in DNA barcoding to catalog local biodiversity, fostering community involvement in science.

Targeting Toxoplasma parasites and their protein accomplices
Researchers identify that a Toxoplasma gondii enzyme drives parasite's survival. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Scavenger protein receptor aids the transport of lipoproteins
Scientists elucidated how two major splice variants of scavenger receptors affect cellular localization in endothelial cells. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

