MCP: This protein makes antibody drugs work
Hundreds of therapeutic antibody drugs target cell-surface molecules in cancers and other diseases. But different patients respond differently to antibody therapy, and doctors struggle to predict who will benefit most.
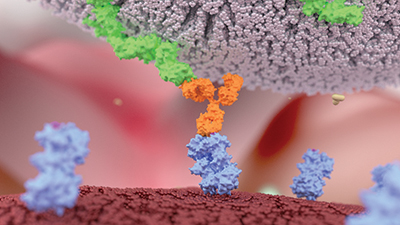
Except for a few used to ferry drugs or toxins to a specific cell population, most antibodies work by recruiting the immune system. When natural killer cells, the body’s tiny assassins, recognize antibodies coating a target cell, the NK cells latch onto the target and kill it.
Kashyap Patel, a grad student at Iowa State University, studies the receptor CD16a, receptor protein on natural killer cells that recognizes and binds to antibodies. Patel and his advisor, Adam Barb, now a professor at the University of Georgia, were interested in changes to CD16a that might underlie binding changes.
“CD16a in our bodies is different than the CD16a that’s used to test monoclonal antibodies,” Patel said. Whereas the recombinant version used in laboratories has limited posttranslational modifications, the human version is glycosylated at five different sites. Glycosylation, which happens in the endoplasmic reticulum, can add complex branched structures to a protein; those modifications can alter proteins’ binding characteristics and could in principle make CD16a more or less likely to bind to antibodies.
Scientists know that a genetic polymorphism near one N-glycosylation site in CD16a can influence how well antibody treatment works. It isn’t clear whether that polymorphism affects glycans directly or whether genetic changes that do affect glycans affect CD16a-antibody binding. Studying the variations in glycan structure at each site is difficult, because isolating enough CD16a from a single person to analyze poses a technical challenge.
In a recent article in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Patel, Barb and colleagues report that they studied post-translational modifications to CD16a in glycopeptide samples harvested from the natural killer cells of individual plasma donors. Then they used glycomics tools to determine the structures of the glycans.
“We weren’t expecting the variability we saw,” Patel said. At five sites in CD16a, the team found substantial variability in the structure of glycans — both among the donors and within each individual.
The researchers don’t know yet what to make of the glycan variability, because the donor pool was small and few studies of this type have been done. However, now that the protocol for studying glycan composition from a single person is worked out, Barb’s lab hopes to determine whether changes to that composition affect the immune system’s response to antibody therapy.
When Patel started this project, he didn’t know much about protein glycosylation, but he said he intends to keep studying it as a postdoctoral fellow.
“Once you see a protein with N-glycans on it, you cannot unsee it. You can’t ignore it.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Using DNA barcodes to capture local biodiversity
Undergraduate at the University of California, Santa Barbara, leads citizen science initiative to engage the public in DNA barcoding to catalog local biodiversity, fostering community involvement in science.

Targeting Toxoplasma parasites and their protein accomplices
Researchers identify that a Toxoplasma gondii enzyme drives parasite's survival. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Scavenger protein receptor aids the transport of lipoproteins
Scientists elucidated how two major splice variants of scavenger receptors affect cellular localization in endothelial cells. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Fat cells are a culprit in osteoporosis
Scientists reveal that lipid transfer from bone marrow adipocytes to osteoblasts impairs bone formation by downregulating osteogenic proteins and inducing ferroptosis. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Unraveling oncogenesis: What makes cancer tick?
Learn about the ASBMB 2025 symposium on oncogenic hubs: chromatin regulatory and transcriptional complexes in cancer.

Exploring lipid metabolism: A journey through time and innovation
Recent lipid metabolism research has unveiled critical insights into lipid–protein interactions, offering potential therapeutic targets for metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Check out the latest in lipid science at the ASBMB annual meeting.

