From the journals: JLR
Predicting drug-induced lysosomal fat buildup. Minimizing side effects of atherosclerosis treatment. Finding a key to sepsis diagnosis and treatment. Read about papers on these topics recently published in the Journal of Lipid Research.
Predicting drug-induced lysosomal fat buildup
The accumulation of phospholipids in lysosomes, called drug-induced phospholipidosis, or DIP, is associated with more than 50 FDA-approved drugs, making it one of the most common forms of drug toxicity. Typically impacting the lungs, liver or kidney, DIP is involved with diseases including pulmonary fibrosis and fatty liver disease.
Due to the serious implications of DIP, physicians terminate drug treatment when it is detected, limiting interventions that might be critical to a patient’s recovery. Despite its prevalence, researchers do not yet clearly understand DIP’s causes and implications, making it difficult to predict if a drug will cause the condition and to separate specific drug targets from downstream effects.
A recent study in the Journal of Lipid Research by Vania Hinkovska–Galcheva and fellow researchers at the University of Michigan Medical School and the University of Michigan identified lysosomal phospholipase A2, or PLA2G15, as a key target of cationic amphiphilic drugs such as amiodarone, which regularly are implicated in phospholipidosis. After assaying libraries of compounds known to cause phospholipidosis as well as drugs not previously reported to do so, the team found that inhibition of this enzyme’s activity, measured by a decrease in 1-O-acylceramide formation, was an excellent candidate for predicting DIP.
While inhibition of PLA2G15 is clear, the researchers do not propose direct enzyme binding as the cause but rather the interference of electrostatic charge interactions between positively charged regions of the enzyme’s lipid-binding domain and negatively charged phospholipid head groups. The team was able to make immediate use of this finding, demonstrating phospholipidosis in vitro for 36 PLA2G15-inhibiting compounds not previously known to cause phospholipidosis. They also identified several drugs known to cause phospholipidosis but not predicted to do so by other models. PLA2G15 inhibition provides a potentially robust tool for toxicity screening during drug development.

Minimizing side effects of atherosclerosis treatment
High levels of very low-density lipoprotein, or VLDL, and low-density lipoprotein, or LDL, which is produced from breaking down VLDL, are associated with the buildup of fats within arteries, causing atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, or ASCVD, a leading cause of death worldwide. Overproduction of VLDL can result from hereditary disease, obesity and insulin resistance, while inhibition of VLDL secretion significantly reduces ASCVD development. Available strategies to inhibit VLDL secretion from the liver typically result in the accumulation of fat inside the liver along with subsequent complications.
In a recent study published in the Journal of Lipid Research, Bingxiang Wang and colleagues at the Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, along with collaborators from the University of Alberta, demonstrated in mice that deficiency in cargo receptor Surfeit 4, or Surf4, not only reduces VLDL secretion and ASCVD development but does so without fat accumulation and liver damage. Additionally, the team found that knockdown of Surf4 reduced plasma cholesterol levels but did not affect the secretion of PCSK9, an enzyme that increases LDL cholesterol plasma levels by degrading a key receptor involved in clearing plasma LDL. The work contributes to researchers’ growing understanding of lipid metabolism regulation and how to minimize side effects of ASCVD treatment.
Lipids: The key to sepsis diagnosis and treatment
Sepsis is an inflammatory disease caused by the body’s extreme reaction to a bacterial or fungal infection. Through a complex cascade of microcirculatory collapse and dysregulated immune response, sepsis rapidly causes tissue damage and organ failure, with mortality increasing by 4% each hour sepsis remains undiagnosed. The diversity of immune and vascular responses combined with multiorgan failure makes sepsis the most common cause of death in hospitalized patients and the biochemical basis extremely difficult to deconstruct. Sepsis treatment is restricted to antibiotics and supportive care, and despite the critical need, researchers have yet to identify clinically relevant and specific diagnostic biomarkers. Lipids may be the answer to both diagnosis and treatment.
As a part of a thematic review series, Kaushalya Amunugama and colleagues at the St. Louis University School of Medicine recently published a review in the Journal of Lipid Research highlighting the importance of dysregulated lipid metabolism in sepsis pathology and of key lipid-regulating enzymes. Many bioactive lipids directly contribute to sepsis progression, while other lipids are byproducts of sepsis-associated metabolic changes. The authors summarize existing evidence of the lipid–sepsis connection in support of presenting lipids as candidates for diagnostic biomarkers as well as targets of therapeutics.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
Liver enzyme holds key to adjusting to high-protein diets
Researchers at the University of Geneva show that glutamate dehydrogenase controls blood alkalinity during fasting.
Adults grow new brain cells
How does the rare birth of these new neurons contribute to cognitive function?
From the journals: JBC
Histone demethylase inhibited by own sequence. MicroRNA reduces cell cycle–related apoptosis. Multipurpose antibiotic takes on staph infections. Read about recent JBC papers on these topics.
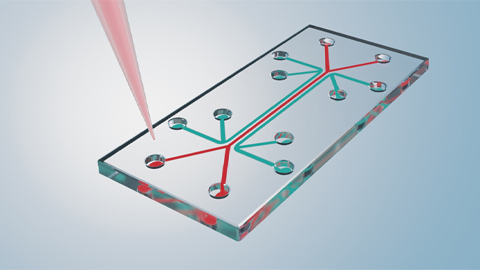
Tiny laboratories that fit in your hand can rapidly identify pathogens using electricity
Pathogens have distinct electrical charges, shapes and sizes. Measuring how quickly they move through an electric field can help researchers separate different species in a sample.
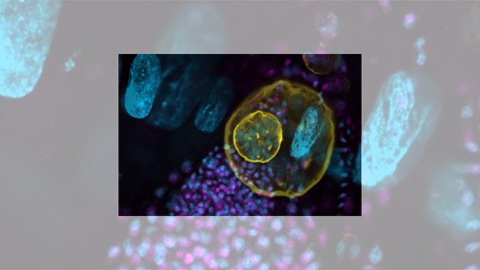
Toxoplasma gondii parasite uses unconventional method to make proteins for evasion of drug treatment
This recent study by a team from Bill Sullivan’s lab at the Indiana University School of Medicine was named a Journal of Biological Chemistry Editor’s Pick.

Of genes, chromosomes and oratorios
Jenny Graves has spent her life mapping genes and comparing genomes. Now she’s created a musical opus about evolution of life on this planet — bringing the same drive and experimentalism she brought to the study of marsupial chromosomes.

