JLR: What controls cholesterol biosynthesis?
Homeostasis is an important biochemical principle. The pace of a biosynthetic pathway often is controlled by feedback from pathway products, adjusting the system to prevent excessive accumulation of its products.
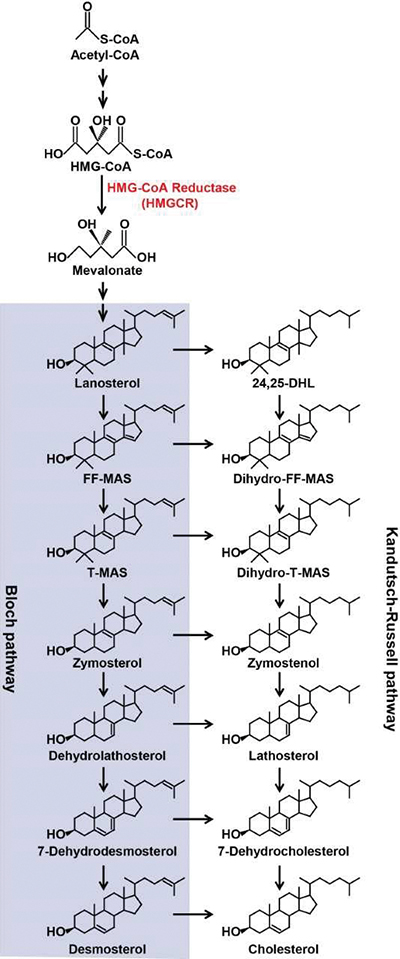 A pathway diagram shows two parallel routes from mevalonate to cholesterol.Bao-Liang Song
A pathway diagram shows two parallel routes from mevalonate to cholesterol.Bao-Liang Song
Cholesterol biosynthesis is one example. Researchers know it is regulated by metabolic intermediates but until now have disagreed about which intermediates do the work. In the Journal of Lipid Research, Liang Chen and colleagues at Wuhan University and the Chinese Academy of Sciences report that several metabolites can affect the activity of two cholesterol biosynthesis enzymes. The study gives new insight into how cholesterol biosynthesis is regulated.
Researchers knew that an intermediate product of the biosynthetic pathway could inhibit each of two control points: HMG-CoA reductase, or HMGCR, which synthesizes a key cholesterol precursor called mevalonate, and sterol responsive element-binding protein, or SREBP, a transcription factor that affects many cholesterol synthesis enzymes.
Data suggested that lanosterol, the first intermediate in the pathway that is cyclic instead of linear, was the key regulator, but the researchers knew that a slightly modified version of lanosterol might be more important. The question is complicated because the cholesterol biosynthesis pathway bifurcates after lanosterol is formed.
In lanosterol or any of its downstream products, a double bond in the molecule’s alkyl tail can be reduced, and the reduced molecules proceed through the same steps to be turned into cholesterol (see figure). So which intermediate cholesterol metabolite exerts the most control over the overall biosynthetic pathway?
That is a technically difficult problem. It is hard to induce accumulation of specific intermediates, because no effective enzyme inhibitors exist for specific steps in sterol synthesis and cells are unlikely to take up exogenously added pathway intermediates.
Chen and colleagues worked around these difficulties by generating a cell line better equipped to absorb mevalonate, a key intermediate produced by HMGCR. In these cells, intermediates can accumulate even if HMGCR activity is blocked. When these cells are provided with mevalonate, they scale up cholesterol production, triggering homeostatic degradation of HMGCR and blocks SREBP activation.
The team then systematically knocked out cholesterol biosynthesis enzymes using CRISPR, forcing traffic to back up immediately upstream of whichever conversion step had been blocked. Using lipidomic analysis of sterol extracts from each knockout cell line, they assessed the impact of loss of each enzyme and accumulation of its substrate, identifying key metabolites that impacted levels of HMGCR and SREBP.
The researchers showed that lanosterol down-regulated HMGCR but not SREBP, confirming that lanosterol and not its reduced relative is the key regulator. They also found that other sterol intermediates with reduced double bonds inhibited both HMGCR and SREBP. The authors say that molecules resembling these endogenous regulators could be a new way to control cholesterol levels.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

When oncogenes collide in brain development
Researchers at University Medical Center Hamburg, found that elevated oncoprotein levels within the Wnt pathway can disrupt the brain cell extracellular matrix, suggesting a new role for LIN28A in brain development.

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

