The many faces of lipins
Glycerolipids are known to be key components of biological membranes in the form of phospholipids as well as a storage reservoir of fatty acids in the form of triacylglycerols. While we have recognized this for some time now, we are still discovering the critical enzymes, and aspects of their regulation, involved in the synthesis of these lipids.
One important step in the synthesis of glycerolipids involves the dephosphorylation of phosphatidic acid resulting in the generation of diacylglycerol. This key branching step determines the fate of glycerol backbones and fatty acids in lipid biosynthesis.
Diacylglycerol can be acylated to triacylglycerol that is stored in lipid droplets via the glycerol phosphate pathway, or it can be condensed with cytidine diphosphate-choline or cytidine diphosphate ethanolamine for the synthesis of the membrane phospholipids phosphatidylethanolamine and phosphatidylcholine (the Kennedy pathway). Phosphatidic acid also is used for the synthesis of other phospholipids, such as phosphatidylinositol and cardiolipin, by condensation with CDP-diacylglycerol.
In addition to these roles in lipid synthesis, phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol now are recognized to play important signaling and structural roles in biological membranes. Therefore, regulation of phosphatidic acid dephosphorylation is critical for several aspects of lipid and membrane homeostasis.
Lipins define a class of Mg2+-dependent phosphatidic acid phosphatases collectively known as PAPs. Lipin 1, the founding member of this widely conserved family in eukaryotes, originally was identified as the gene mutated in fatty liver dystrophy mice. These mice display a lipodystrophic phenotype characterized by fatty livers and hypertriglyceridemia.
The demonstration that lipins are in fact PAP enzymes came later, when PAP was purified from budding yeast and found to be a member of the lipin family. Fungi, nematodes and insect genomes each encode one lipin, while human genomes encode three: lipin 1 (the paralogue that has attracted most attention so far), lipin 2 and lipin 3. Research in a multitude of model organisms has advanced our knowledge over the past 10 years, uncovering many surprising aspects of lipin biology and raising intriguing questions regarding their function and regulation.
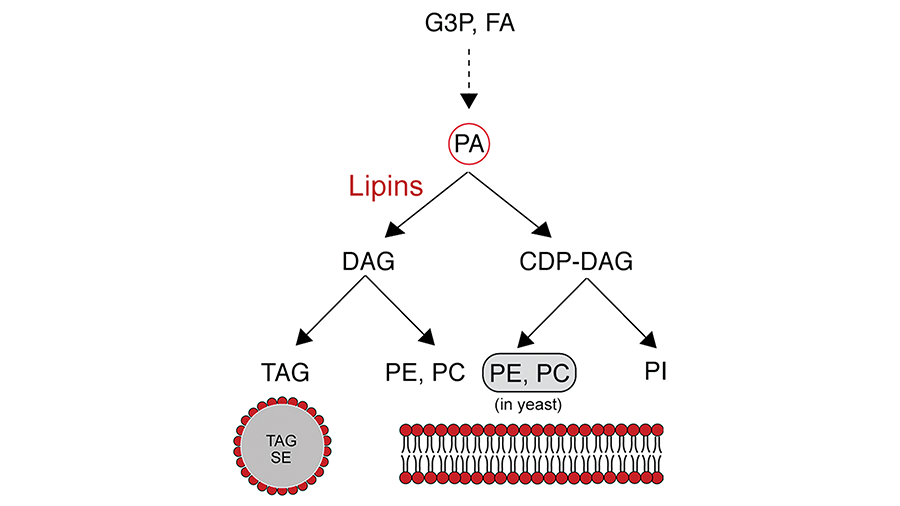 Lipid metabolic roles of lipins
Lipid metabolic roles of lipins
Unlike the other enzymes of the triacylglycerol biosynthetic pathway, lipins lack transmembrane domains and exhibit in most cells a primarily soluble distribution. As a consequence, lipin membrane targeting is a key regulatory step in triacylglycerol metabolism.
Lipins are sequestered in the cytosol via hyperphosphorylation via growth/nutrient or cell-cycle-dependent phosphorylation catalysed by several kinases, such as TOR in mammals and Pho85 or Cdc28, among others, in yeast (See Choi, H.S et al 2012 and Choi, H.S et al 2011).
A highly conserved transmembrane phosphatase complex, originally described in yeast, mediates activation of lipins and their association with membranes (See Santos-Rosa, H et al 2005 and Karanasios, E et al 2010).
Recent studies have highlighted additional control of the membrane-bound lipins: Cytosolic pH via electrostatic interaction between phosphatidic acid and lipin 1 and proteasome-mediated degradation of active lipin in yeast cells are important determinants of PAP levels. Such multilevel regulation may allow lipins to modulate phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol levels on different membranes.
Indeed, in addition to their biosynthetic roles in the endoplasmic reticulum, yeast and mammalian lipins also have roles in mitochondria, lipid droplets, nuclear membrane, vacuoles and the autophagosome.
The physiological consequences of lipin dysfunction are emerging as an area of intense and exciting research.
As alluded to above, lipins are critical for triacylglycerol synthesis in yeasts, plants, worms and flies. Rodent models of lipin 1 deficiency display a lipodystrophic phenotype characterized by significant reduction in fat mass and lack of adipocyte differentiation. It also turns out that lipins are essential for maintenance of nuclear structure and endoplasmic reticulum membrane organization, suggesting that their dysfunction also could affect metabolic homeostasis through structural mechanisms.
Surprisingly, deleterious mutations in lipin 1 do not affect fat distribution in humans but instead cause severe myopathy in the form of rhabdomyolysis. Recently, this has been proposed to result from defective lipin 1-mediated autophagic clearance in muscle. The basis for the different fat pathologies between rodent models and humans remains a critical question to be answered.
Perhaps the most unexpected aspect of lipins is that they have a distinct intranuclear pool in many cell types. For example, lipin 1 can regulate expression of genes encoding fatty-acid metabolic enzymes via physical interactions with components of the transcription machinery. The presence of a nuclear PAP enzyme raises many intriguing questions.
One unresolved issue is whether the localization and function of lipin in the nucleus is linked somehow to its role in modulating lipid metabolism in the cytoplasm. It is also not known whether nuclear PAP affects nuclear membrane biogenesis and nuclear signalling.
Given the emerging roles of the nuclear envelope in gene expression, lipins could control transcription through lipid remodelling at the nuclear membrane. For example, nuclear import of lipin 1 in response to nutrient depletion causes nuclear envelope remodelling, which down-regulates the major lipogenic factor SREBP (short for sterol regulatory element-binding protein) through unknown mechanisms.
While we’ve learned a lot about lipins, it is clear that there are many remaining questions. Addressing these questions will be vital to understanding the mechanisms that underlie the emerging roles of lipins in cellular and organismal homeostasis.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
Liver enzyme holds key to adjusting to high-protein diets
Researchers at the University of Geneva show that glutamate dehydrogenase controls blood alkalinity during fasting.
Adults grow new brain cells
How does the rare birth of these new neurons contribute to cognitive function?
From the journals: JBC
Histone demethylase inhibited by own sequence. MicroRNA reduces cell cycle–related apoptosis. Multipurpose antibiotic takes on staph infections. Read about recent JBC papers on these topics.
Tiny laboratories that fit in your hand can rapidly identify pathogens using electricity
Pathogens have distinct electrical charges, shapes and sizes. Measuring how quickly they move through an electric field can help researchers separate different species in a sample.
Toxoplasma gondii parasite uses unconventional method to make proteins for evasion of drug treatment
This recent study by a team from Bill Sullivan’s lab at the Indiana University School of Medicine was named a Journal of Biological Chemistry Editor’s Pick.

Of genes, chromosomes and oratorios
Jenny Graves has spent her life mapping genes and comparing genomes. Now she’s created a musical opus about evolution of life on this planet — bringing the same drive and experimentalism she brought to the study of marsupial chromosomes.

