At the interface
Sphingolipids, or SLs, have emerged as critical players in membrane stability and as essential signaling molecules. SLs range from abundant species involved in maintaining membrane integrity, such as sphingomyelin, to scarce and potent signaling species, such as sphingosine-1-phosphate, or S1P. S1P mediates critical signaling functions through interaction with its cognate G-protein coupled receptors in development and in several disease states. In recent decades, many resources have been devoted to understanding how S1P generation is regulated.
S1P can be generated through the action of two sphingosine kinase isoforms. The more commonly expressed of the two is sphingosine kinase 1, or SK1. This enzyme has garnered attention as a potential therapeutic target, as it often is upregulated in diseases such as cancer. To gain access to its substrate, sphingosine, and to release its product, S1P, SK1 must interact directly with membranes. However, how SK1 achieves membrane binding has been contested in the literature. How does a cytosolic lipid-metabolizing enzyme without any lipid-binding domains interact with membranes to access its substrate?
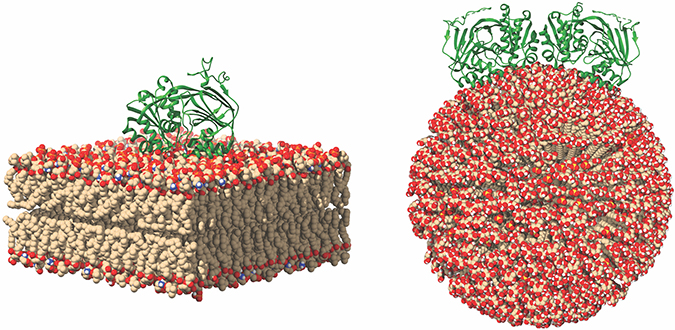 This image of SK1 binding to membranes shows potential SK1 membrane binding poses for SK1 in the presence of flat and curved membranes. Michael Pulkoski-Gross
This image of SK1 binding to membranes shows potential SK1 membrane binding poses for SK1 in the presence of flat and curved membranes. Michael Pulkoski-Gross
Previously, researchers thought SK1 translocation was dependent on other proteins. However, recent data show how SK1 can bind directly to membranes. SK1 possesses an intrinsic interface composed of two motifs: one electrostatic motif and one hydrophobic motif. Using biochemical methods, we found that these two motifs are necessary for membrane interaction, thus implicating their function as a single entity. Using hydrogen deuterium exchange mass spectrometry, we confirmed that SK1 employs a single contiguous interface that contains the two motifs. In cancer cells, disruption of this interface causes loss of membrane association and decreases SK1 activity. Past research has shown that interaction with membranes is critical for mediating SK1-dependent biologies including tumor cell invasion and endocytosis. This could provide a new avenue for targeting SK1 in diseases. Inhibition of membrane binding would deny SK1 access to its substrate, thereby inhibiting all activity.
Recent research shows an important role for SK1 in endocytic trafficking. SK1 presence at endocytic membranes would require membrane binding and curvature sensing. However, how SK1 can do this is largely unknown. Analysis of the atomic structure of SK1 revealed a potential dimerization interface. Such dimerization would align the membrane-binding interface of each SK1 monomer. This would strengthen the interaction and potentially allow for physical curvature sensing by SK1. This remains to be validated, but it’s an exciting hypothesis. Another way to potentially inhibit activity would be to inhibit dimerization, if that is required for activity and membrane binding.
Significant strides have been made in understanding the structure and function of many SL metabolizing enzymes, and exciting questions remain to be answered, especially for SK1. How can SK1 decipher the difference between the charges of different anionic phospholipids? How does the catalytic cycle progress once SK1 is at the membrane? Is dimerization required for membrane binding/curvature sensing? What role is the hydrophobic patch playing in curvature sensing?
Biophysical, biochemical and structural research will reveal the secrets of how SL enzymes work and how they might be exploited for therapeutic development.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.


