Can probiotics change fish behavior?
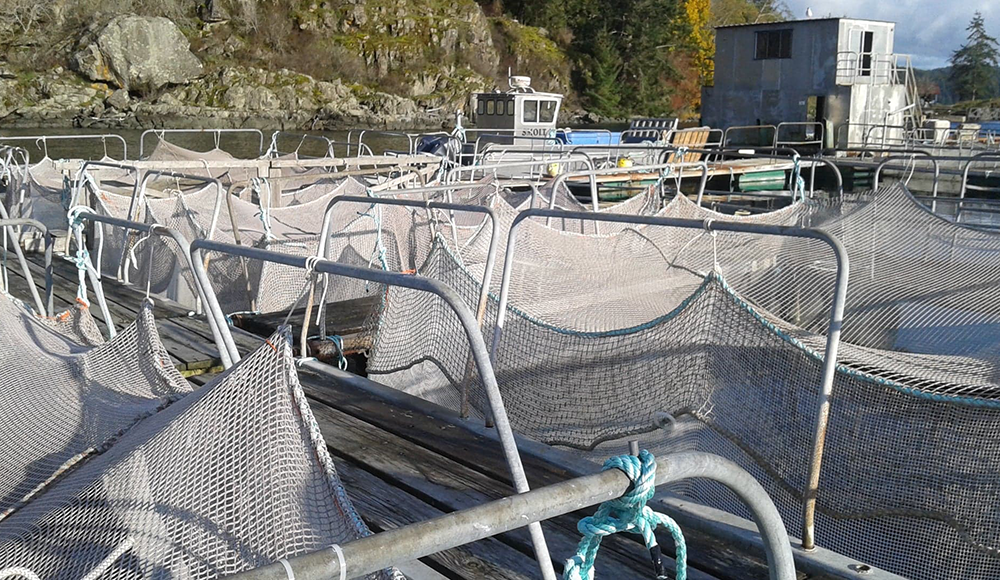


Frank and her colleagues in Christina Semeniuk’s lab and comentor Daniel Heath’s lab at the University of Windsor in Ontario are trying to determine whether an unlikely intervention — a probiotic supplement in fish food — might help triploid Chinook salmon fare better. They’re starting with how the fish behave.
“Behavioral flexibility and sensitivity … would be an immediate measure for physiological (and neural genomic) change, given the connections between the gut–brain–behavior axis,” Semeniuk said.
Frank tested how probiotic supplements added to fish food affected the way hundreds of fingerling diploid and triploid fish respond to novel stimuli such as a glass bead tossed into the tank, a predator-shaped dummy passing overhead and an approaching human researcher. She will present her work as part of the Genomics poster session during the 2021 ASBMB annual meeting; you can see her talk and post questions while the meeting is underway.
In the future, Frank plans to integrate transcriptomic analyses with her behavioral studies, an approach known as behavioral genomics. Little is known about how triploidy affects genes related to learning and memory, so even if probiotics have little effect, she stands to learn something interesting.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Cracking cancer’s code through functional connections
A machine learning–derived protein cofunction network is transforming how scientists understand and uncover relationships between proteins in cancer.

Gaze into the proteomics crystal ball
The 15th International Symposium on Proteomics in the Life Sciences symposium will be held August 17–21 in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
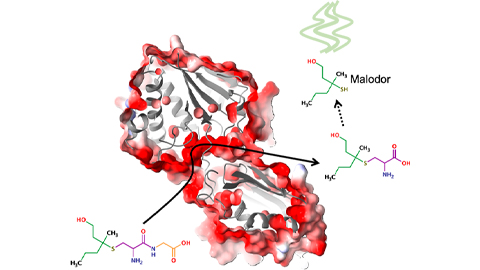
Bacterial enzyme catalyzes body odor compound formation
Researchers identify a skin-resident Staphylococcus hominis dipeptidase involved in creating sulfur-containing secretions. Read more about this recent Journal of Biological Chemistry paper.

Neurobiology of stress and substance use
MOSAIC scholar and proud Latino, Bryan Cruz of Scripps Research Institute studies the neurochemical origins of PTSD-related alcohol use using a multidisciplinary approach.
Pesticide disrupts neuronal potentiation
New research reveals how deltamethrin may disrupt brain development by altering the protein cargo of brain-derived extracellular vesicles. Read more about this recent Molecular & Cellular Proteomics article.

A look into the rice glycoproteome
Researchers mapped posttranslational modifications in Oryza sativa, revealing hundreds of alterations tied to key plant processes. Read more about this recent Molecular & Cellular Proteomics paper.

