
Biochemists bite back
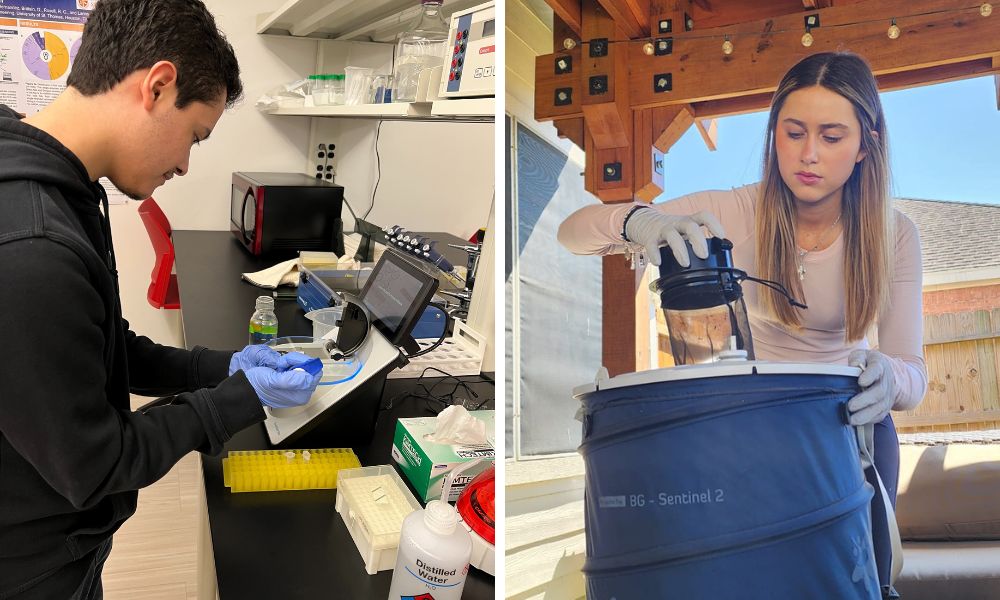
During the hot summer months in Houston, citronella candles, bug sprays, zappers and fly swatters sell like hotcakes so people can keep mosquitos at bay. However, students at a local university invite the pests into their backyards. Using large barrel traps, they have collected hundreds of mosquitos to investigate what viruses the insects are spreading in the Bayou City and across the Lone Star State.
Mosquitos, ticks and fleas, also known as vectors, carry myriad viruses, bacteria and parasites. These pests transmit pathogens to animals and humans via their saliva during a bite. But don’t worry too much: The chance of developing a viral disease, such as West Nile virus, after a mosquito bite is just one in 300 in the U.S.

However, the mosquito population in North America has increased 10-fold over the past 50 years due to climate change. Now, health officials are seeing some viruses that previously were found in only tropical regions a decade ago pop up across the southern U.S.
“Even though the field of microbiology has been around for centuries, it's only now that we're beginning to uncover much of its diversity,” Maia Larios, professor and chair of biology at the University of St. Thomas and project supervisor, said.
Therefore, researchers at UST began to do their part in tracking mosquito species and the viruses they carry across Houston.
“Knowing where viruses exist and how they might move to new environments or new hosts is important for better surveillance, tracking and prevention of known diseases, as well as emergent and novel diseases that might challenge humans in the future,” Ava Ngo, an undergraduate researcher at UST, said.
Ngo worked with fellow undergraduates Angelika Jordan and William Maldonado to capture mosquitos across town. Their traps are designed to simulate a human being by imitating the visual signals and convection currents of a body.
After capturing the mosquitos and extracting their RNA and DNA, the team worked with the UST computer science department to perform metagenomics on the samples. The hundreds of mosquitos they gathered collectively carried dozens of viruses, such as West Nile virus, Dengue virus and others.
According to Rosemarie Rosell, a professor of biology at UST and project supervisor, the most surprising virus they uncovered was Lauvirus, which is native to Southeast Asia.
“Lauvirus interests me the most, because Houston is right on the shipping channel,” Rosell said.

The Houston Ship Channel stretches 52 miles, starting at the Gulf of Mexico and ending just four miles east of downtown.
“We have all these ginormous shipping containers come in on ships from all over the world,” Rosell said. “These containers have water inside them, which can carry mosquitos with different types of viruses and viral loads.”
The team also found that different mosquito species localized to specific parts of the Houston metro area. In the wooded north, Aedes aegypti mosquitos dominate, and Culex quinquefasciatus mosquitos primarily inhabit the south.
In addition to finding viruses with known genomes, the team identified thousands of uncharacterized viral sequences, which they plan to investigate in future studies.
“We are filling in gaps in our understanding of diversity in nature, which ties into health and conservation and affects the human existence,” Larios said. “It’s not just about the ‘sexy’ diseases, but it is also about understanding what kinds of viruses exist in the environment and how they move.”
Details
Ava Ngo will present this research from 5:30 to 6:30 p.m. CDT on Monday, March 25, at Discover BMB 2024, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology annual meeting in San Antonio. Her poster is at Board 301.
Abstract title: Characterizing Houston’s viral strains carried by mosquitos via metagenomics
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Targeting Toxoplasma parasites and their protein accomplices
Researchers identify that a Toxoplasma gondii enzyme drives parasite's survival. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Scavenger protein receptor aids the transport of lipoproteins
Scientists elucidated how two major splice variants of scavenger receptors affect cellular localization in endothelial cells. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Fat cells are a culprit in osteoporosis
Scientists reveal that lipid transfer from bone marrow adipocytes to osteoblasts impairs bone formation by downregulating osteogenic proteins and inducing ferroptosis. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Unraveling oncogenesis: What makes cancer tick?
Learn about the ASBMB 2025 symposium on oncogenic hubs: chromatin regulatory and transcriptional complexes in cancer.

Exploring lipid metabolism: A journey through time and innovation
Recent lipid metabolism research has unveiled critical insights into lipid–protein interactions, offering potential therapeutic targets for metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases. Check out the latest in lipid science at the ASBMB annual meeting.
Melissa Moore to speak at ASBMB 2025
Richard Silverman and Melissa Moore are the featured speakers at the ASBMB annual meeting to be held April 12-15 in Chicago.

