
Mining millets
Millets are ancient grains and cereals with origins in Africa, the Middle East and Asian countries including China and India, where they are food staples. In addition to growing in harsh environments and enduring drought or attacks by pests, millets are often less processed and yield higher nutritional benefits than grains such as corn, rice and wheat.

Those conventional grains of the Western diet are well studied, but scientists know little about the bioactive food species in major and minor millets, including the distribution of lipids, or fat-soluble compounds; the composition of fatty acids, or lipid building blocks; and the presence of nutraceuticals, or substances in millets and food that benefit physiological health.
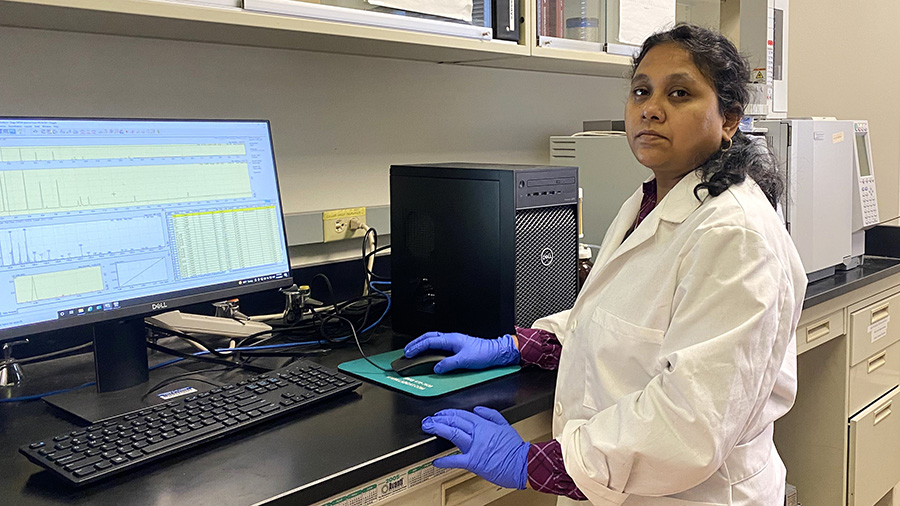
Sugasini Dhavamani, a research assistant professor at the University of Illinois at Chicago, and her team have studied the nutri-lipidomic profiles of major and minor millet seeds and oils.
“I am passionate about lipid research,” Dhavamani said, “I love working at the University of Illinois because we have amazing equipment and facilities, and great means for collaboration.”
The oils of grains are not commercially available, so the researchers first extracted lipids from the millets, then analyzed samples using high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry.
“The oil extraction takes time,” Dhavamani said, adding that the researchers face other challenges. “After extraction we often get a low quantity of lipids, which can also cause difficulty. Stability is a concern because the lipids are easily oxidized.”

After profiling sorghum millet, little millet, finger millet, proso millet, kodo millet, pearl millet and foxtail millet, Dhavamani and colleagues found that oleic acid, linoleic acid and alpha-linoleic acid, or omega-9,-6 and -3, are the three major fatty acid species present in millets and seed oils.
“Most of the millets evaluated contained omega-9 and omega-6 and a small amount of omega-3 fatty acids, which help to lower cholesterol and blood pressure levels, and can benefit chronic disease,” Dhavamani said. “Millets also have nutraceuticals, which are helpful for lowering inflammation.”
In the future, the researchers want to expand this work into animal models, where Dhavamani can assess the health benefits of millet consumption, followed by examining proteomics and metabolomics of millets; however, experiments of this scale require increased funding.
Details
Sugasini Dhavamani will present this research from 5:30 to 6:30 p.m. CDT on Sunday, March 24, at Discover BMB 2024, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology annual meeting in San Antonio. Her poster will be at board 326.
Abstract title: Nutri-lipidomics, bioactive lipids and antioxidant potential of major and minor millet seed and oil — a novel approach
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
CRISPR epigenome editor offers potential gene therapies
Scientists from the University of California, Berkeley, created a system to modify the methylation patterns in neurons. They presented their findings at ASBMB 2025.

Finding a symphony among complex molecules
MOSAIC scholar Stanna Dorn uses total synthesis to recreate rare bacterial natural products with potential therapeutic applications.

E-cigarettes drive irreversible lung damage via free radicals
E-cigarettes are often thought to be safer because they lack many of the carcinogens found in tobacco cigarettes. However, scientists recently found that exposure to e-cigarette vapor can cause severe, irreversible lung damage.

Using DNA barcodes to capture local biodiversity
Undergraduate at the University of California, Santa Barbara, leads citizen science initiative to engage the public in DNA barcoding to catalog local biodiversity, fostering community involvement in science.

Targeting Toxoplasma parasites and their protein accomplices
Researchers identify that a Toxoplasma gondii enzyme drives parasite's survival. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Scavenger protein receptor aids the transport of lipoproteins
Scientists elucidated how two major splice variants of scavenger receptors affect cellular localization in endothelial cells. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

