
Biochemists face the climate challenge
Everyone knows coral bleaching occurs when seawater gets hot. Biochemists ask: How?
Corals die when their photosynthetic algal symbionts experience heat stress and exude hydrogen peroxide, causing coral tissue to expel the algae. Thus, coral bleaching is a biochemical process that we can understand and engage with, imagining new solutions to climate changes that degrade our planet.
Submit an abstract
Abstract submission begins Sept. 14. If you submit by Oct. 12, you'll get a decision by Nov. 1. The regular submission deadline is Nov. 30. See the categories.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have long embraced “One Health,” the concept that a healthy planet is required for human health. Recently, the National Institutes of Health launched their Climate Change and Health Initiative. Biochemistry is central to preserving the natural world and developing fully renewable building materials, novel foods and health care solutions.
This session will explore how the living world experiences changes in temperature, pH, salt, nutrients, desiccation and other conditions. The speakers will illuminate the cell and molecular mechanisms underlying coral symbiosis, thermal adaptations of marine organisms, temperature-dependent mutagenesis and transposition in the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans, and the endocrine underpinnings of environmental influences on human health. This session is for the next generation of biochemists who will meet the climate challenge.
Keywords: One Health, thermal adaptation, symbiosis.
Who should attend: The next generation of biochemists who will save the planet.
Theme song: “Imagine” by John Lennon
This session is powered by the courage to face humanity’s greatest challenge.

Biochemistry and climate change
Asiya Gusa, Duke University
James A. DeMayo, University of Colorado–Denver
Yixian Zheng, Carnegie Institution for Science
Teresa Horton, Northwestern University
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Defeating deletions and duplications
Promising therapeutics for chromosome 15 rare neurodevelopmental disorders, including Angelman syndrome, Dup15q syndrome and Prader–Willi syndrome.
Using 'nature’s mistakes' as a window into Lafora disease
After years of heartbreak, Lafora disease families are fueling glycogen storage research breakthroughs, helping develop therapies that may treat not only Lafora but other related neurological disorders.

Cracking cancer’s code through functional connections
A machine learning–derived protein cofunction network is transforming how scientists understand and uncover relationships between proteins in cancer.

Gaze into the proteomics crystal ball
The 15th International Symposium on Proteomics in the Life Sciences symposium will be held August 17–21 in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
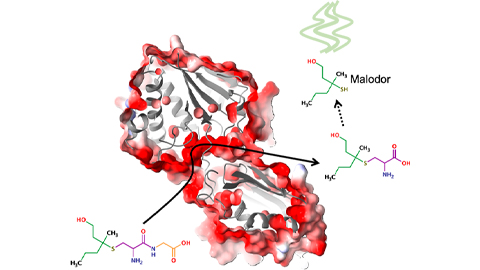
Bacterial enzyme catalyzes body odor compound formation
Researchers identify a skin-resident Staphylococcus hominis dipeptidase involved in creating sulfur-containing secretions. Read more about this recent Journal of Biological Chemistry paper.

Neurobiology of stress and substance use
MOSAIC scholar and proud Latino, Bryan Cruz of Scripps Research Institute studies the neurochemical origins of PTSD-related alcohol use using a multidisciplinary approach.


