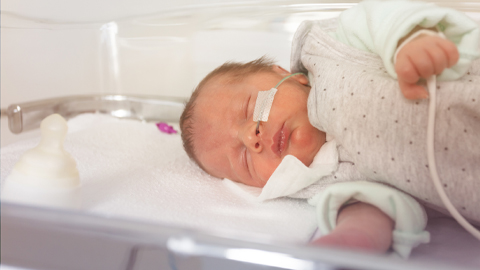
New surfactant could improve lung treatments for premature babies
Scientists have developed a new lung surfactant that is produced synthetically rather than relying on the use of animal tissues. With further development, the formulation could provide a cheaper and more readily available alternative to Infasurf, a medication used to prevent and treat respiratory distress in premature babies.
Surfactants are substances that decrease surface tension where liquids interface with other liquids, gases or solids. In addition to their use in medicines, they are found in a wide range of products including detergents, cosmetics, motor oils and adhesives.
Suzanne Farver Lukjan, a lecturer in chemistry at Troy University in Alabama, led the work.
“A synthetic surfactant could potentially have a longer shelf life, lower production costs, have less batch variability and pose less risk of an immune response compared to animal-derived lung surfactants,” she said. “We hope our formulation will one day be used in hospitals.”
Lukjan will present the research at Discover BMB, the annual meeting of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, which is being held March 23–26 in San Antonio.
Lung surfactants help premature babies breathe while their lung cells finish developing. In addition to offering a potential alternative to replace Infasurf for babies, researchers say the new synthetic surfactant could be useful for treating adults with lung injuries as a result of diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder, miner’s lung or emphysema.
Researchers have previously attempted to develop synthetic lung surfactants, but some have been removed from the market and others have not been able to lower surface tension as well as animal-derived formulations.
In the new work, Lukjan’s team created candidate surfactants from synthetic lipids (fats) and peptides (short chains of amino acids) and then tested their surface-tension-lowering capabilities. They aimed to mimic the composition, lipid phase behavior and biophysical function of Infasurf as closely as possible.
After tweaking a step in the sample preparation process, the researchers found a few formulations that showed particular promise. Although tests demonstrated that the chemical behavior of the synthetic surfactants was quite different from that of Infasurf, the new surfactants were able to mimic the drug’s functionality in terms of lowering surface tension and seem to achieve the optimal range in terms of peptide concentration.
As a next step, Lukjan said, the group plans to continue to refine and test their formulation to further optimize the combination of lipids and peptides. The surfactant would also need to undergo safety testing before it could be used clinically.
This work was partially funded by ONY Biotech Inc., maker of Infasurf.
Suzanne Lukjan will present this research from 4:30 to 6:30 p.m. CDT on Monday, March 25, in the exhibit hall of the Henry B. González Convention Center (Poster Board No. 210) (abstract).
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Building better tools to decipher the lipidome
Chemical engineer–turned–biophysicist Matthew Mitsche uses curiosity, coding and creativity to tackle lipid biology, uncovering PNPLA3’s role in fatty liver disease and advancing mass spectrometry tools for studying complex lipid systems.

Redefining lipid biology from droplets to ferroptosis
James Olzmann will receive the ASBMB Avanti Award in Lipids at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Women’s health cannot leave rare diseases behind
A physician living with lymphangioleiomyomatosis and a basic scientist explain why patient-driven, trial-ready research is essential to turning momentum into meaningful progress.

Life in four dimensions: When biology outpaces the brain
Nobel laureate Eric Betzig will discuss his research on information transfer in biology from proteins to organisms at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Fasting, fat and the molecular switches that keep us alive
Nutritional biochemist and JLR AE Sander Kersten has spent decades uncovering how the body adapts to fasting. His discoveries on lipid metabolism and gene regulation reveal how our ancient survival mechanisms may hold keys to modern metabolic health.

