Inflammation and diabetic kidney disease: Why mitochondria matter
Diabetes mellitus refers to a group of chronic conditions that affect the body’s ability to effectively use sugar, specifically glucose, resulting in a buildup of sugar in the blood. In 2022, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimated that 11.3% of the U.S. population was diabetic and that 38% of adults over age 18 and 49% of adults over 65 were prediabetic, meaning they had higher-than-normal blood glucose levels.

The long-term health effects of diabetes mellitus can be grim. In addition to deteriorating vision, nerve damage and hearing impairment over time, diabetes can also affect larger organ systems. In the U.S., it is the predominant risk factor for cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Diabetics are at increased risk for hypertension, heart attack and stroke; furthermore, one in three diabetic adults have diabetic kidney disease, or DKD.
In DKD, prolonged elevated glucose in the blood damages blood vessels and nephrons, the cells in the kidney responsible for filtration. Often occurring in parallel with ailments such as high blood pressure, DKD damages kidneys increasingly over time. A recent study in the Journal of Biological Chemistry demonstrated a potential to mitigate this damage by improving the function of mitochondria, a cellular organelle responsible for maintaining and generating energy.
Komuraiah Myakala, a research instructor at Georgetown University, uses animal models that mimic Type 2 diabetic disease progression, known as db/db mice, when testing his hypotheses for DKD.
“We have to pick the right model to understand the disease,” Myakala said. “Every metabolic disease is regulated by different signaling pathways; we need to understand, if there is, a causal relationship in kidney disease progression, and the signaling proteins involved.”
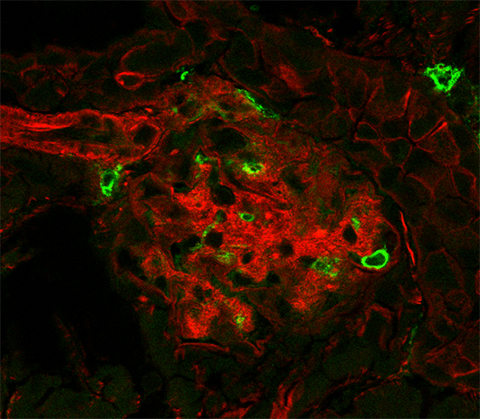
During the study, db/db and healthy mice were given the supplement nicotinamide riboside, or NR. Also known as vitamin B3, NR is a precursor to the biologically functional form of nicotinamide adenine nucleotide, or NAD+, and can increase its levels within the body. A critical co-enzyme in metabolic processes, NAD+ is ubiquitous to every cell type, where it is essential to mitochondria metabolism and generating cellular energy.
The body naturally produces NAD+. With age, levels decline naturally, and low NAD+ also occurs with conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease and neurological disorders.
“The etiology of kidney disease between diabetes and aging are very different,” Myakala said. “Diabetes is usually a higher-grade kidney disease compared to age alone.”
Inflammation is closely associated with damage to the mitochondria, and diabetic kidney disease. Giving NR to the db/db mice reduced inflammation and prevented many of the usual manifestations of kidney decline, for example, levels of blood-protein markers that rise in DKD progression were reduced after NR treatment.
This research helps demonstrate the importance of mitochondrial function in renal disease, particularly in diabetes. Researchers still do not fully understand the mechanisms that link mitochondria and inflammatory disease, and they require further study. This research provides insight, however, into the potential of using supplemental NR to improve mitochondrial function and gives hope for DKD treatment.
Myakala describes his dedication to understanding the mechanisms of kidney disease as “unwavering.” He and his colleagues hope to continue their research as they seek to bridge the gap in understanding that exists between inflammation, mitochondria and kidney disease.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

