JLR: Study sheds light on function of mysterious PCSK9 mutation
High levels of low-density lipoproteins, parcels of lipids and proteins that carry cholesterol, are a leading risk factor for heart disease. Many cholesterol medications lower LDL, some of them by targeting the protein PCSK9.
Scientists at the University of California, San Francisco, have published an investigation in the Journal of Lipid Research into why experiments on PCSK9 give different results in a test tube than they do in liver cells. What they found may explain how a mutation in PCSK9 that long has puzzled scientists leads to heart disease.
Ordinarily, the LDL receptor on the surface of liver cells is responsible for suctioning low-density lipoproteins out of the blood. But after being torpedoed by PCSK9, LDL receptor is brought into the cells and broken down, making the liver less able to control LDL in the bloodstream.
“We have very effective and safe therapies at reducing PCSK9 function,” said John Chorba, a cardiologist and researcher at UCSF. Perhaps you’ve heard of them: Praluent and Repatha are drugs that lower patients’ cholesterol by blocking the interaction between PCSK9 and the LDL receptor.
“But they’re antibody-based approaches,” Chorba said, “and are very expensive. Having a more thorough understanding of how PCSK9 works gives us new opportunities to develop drugs which could be more cost-effective.”
Chorba, who splits his time between lab and clinic, worked with medical student Adri Galvan to understand better the biochemistry of the PCSK9/LDL receptor interaction.
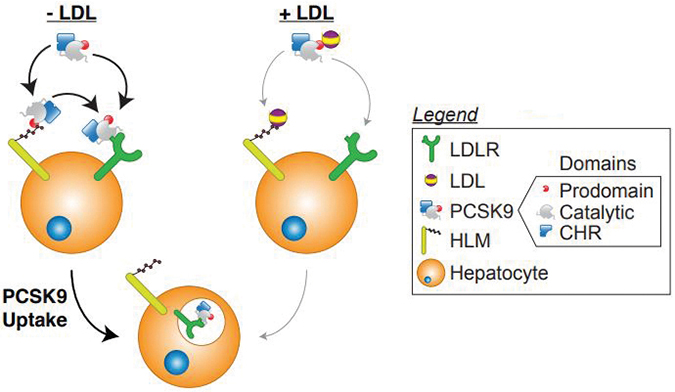 When LDL is absent (left), PCSK9 is likely to bind to the LDL receptor (green) and promote its internalization. When LDL is added, that binding is reduced. But in either case, PCSK9 can bind to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (yellow), which promote PCSK9/LDL receptor binding.John Chorba & Adri Galvan In a test tube, LDL particles block the interaction between the LDL receptor and PCSK9. This sounds like a good thing; the more LDL you have in circulation, the more you would want the LDL receptor to work, and the less you would want PCSK9 to disrupt it.
When LDL is absent (left), PCSK9 is likely to bind to the LDL receptor (green) and promote its internalization. When LDL is added, that binding is reduced. But in either case, PCSK9 can bind to heparan sulfate proteoglycans (yellow), which promote PCSK9/LDL receptor binding.John Chorba & Adri Galvan In a test tube, LDL particles block the interaction between the LDL receptor and PCSK9. This sounds like a good thing; the more LDL you have in circulation, the more you would want the LDL receptor to work, and the less you would want PCSK9 to disrupt it.
But when Chorba and Galvan repeated the experiment in cells, the results showed that the relationship is more complicated. In cells, LDL does not seem to disrupt the interaction as effectively.
“That’s when we really started to ask, what else is going on with these cells?” Galvan said. “What else is PCSK9 interacting with?”
Chorba said, “We thought there must be something (on the cells) that was attenuating that effect.”
Around the time Chorba and Galvan were trying to identify the mystery interactor, a Danish group at Aarhus University published its finding that heparan sulfate proteoglycans, extracellular proteins with a particular sugar chain attached, can help PCSK9 reach the LDL receptor.
Chorba and Galvan confirmed that in cells from which that sugar chain had been cleaved, the LDL receptor/PCSK9 interaction on the surface of cells could be disrupted by LDL, similar to what happened in a test tube.
This led them to a clue about how a long-known but poorly understood mutant form of PCSK9 might work. It’s called the S127R mutation, because it changes the 127th amino acid in PCSK9, serine, into arginine.
“S127R was the initial mutation discovered in PCSK9 as a cause of genetic familial hypercholesterolemia, but the way it worked has been unknown for years,” Chorba said.
S127R is a head scratcher because the change in its amino-acid sequence disrupts PCSK9 maturation. You’d expect the change to reduce total PCSK9, which would reduce LDL, and that should be good for carriers of the gene. But instead, the mutant raises LDL cholesterol levels, putting patients at elevated risk of heart disease.
Chorba and Galvan found that while removing heparan sugar chains from cultured liver cells affected how the cells’ LDL receptors bound to wild-type PCSK9, it affected their interaction with the mutant even more. That suggested that S127R PCSK9 might be interacting more strongly with HSPG — and offered a potential way for the mutant PCSK9 to interact more strongly with LDLR.
“I would imagine that S127R PCSK9 would be more likely to bind to the surface of (liver cells),” Chorba said. “So the local concentration of PCSK9 would be higher … and it would be more likely to run into an LDL receptor that would get internalized and degraded.”
It remains to be seen whether this explanation holds up to further experimental scrutiny. If it does, then future drugs that disrupt the PCSK9/heparin sulfate proteoglycan interaction, which a spinoff company from Aarhus University is working to develop, could be especially effective for people with familial hypercholesterolemia who carry the S127 mutation.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

