In memoriam: Alexander Glazer
Alexander Glazer, a renowned biochemist and environmentalist, died July 18. He was 86.
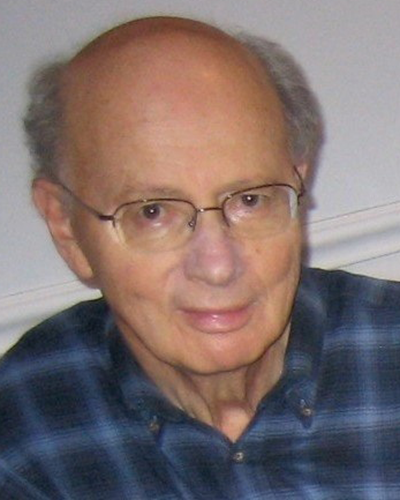

Glazer was born in Poland on July 7, 1935, and immigrated to Australia with his mother after World War II. He earned both his bachelor’s and master’s degrees in biochemistry from the University of Sydney, where he also met Eva Warner who he married in 1958.
While working toward his master’s degree, Glazer attended a lecture given by biochemist Emil Smith from the University of Utah. Inspired by the research and the Southwest’s landscape, Glazer moved to Utah for his doctoral degree and researched the physiochemical properties of proteins under Smith until 1960.
Glazer continued to navigate the globe for his postdoctoral work. He completed postdoctoral fellowships at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel and under Frederick Sanger at the Medical Research Council Laboratory of Molecular Biology in England. His former thesis advisor Smith recruited him to UCLA as faculty in 1964 and he subsequently moved to the University of California, Berkeley in 1976.
Much of Glazer’s early research focused on chemical modifications of proteins and the properties of enzymes including proteases and hydrolyses. With collaborators, he helped determine the structure of phycobiliproteins — light-harvesting structures found in photosynthetic cyanobacteria and certain algae. Through these studies, they were able describe how light energy is transferred to the reaction center in the cell. Glazer then demonstrated how these proteins could be used as fluorescent tags, which are now used to mark and sort living cells in the laboratory.
Glazer also recognized the advantage of what became known as “big data” and worked with statistician Peter Bickel to explore amino acid sequence conservation within protein families and understand how it relates to protein structure and function using publicly available protein sequence databases. Glazer retired from research in 1994 but continued to serve as co-chair of the department of molecular and cell biology at UC Berkeley and as a professor in the graduate school until 1997.
Glazer’s career took a turn when he was hired as the director of the University of California Natural Reserve System, which encompasses a network of field stations and protected natural lands. As director, he focused on pressing issues of environmental science such as nitrogen fixation, contamination of freshwater sources and the repercussions of oil production and use. He served as the system’s director for 11 years.
Glazer received numerous awards and honors throughout his career, including two Guggenheim fellowships, the Endeavor Prize from the British Association for the Advancement of Science, and election to the American Academy of Arts and Sciences and the National Academy of Sciences.
According to an obituary from the NRS, Glazer enjoyed hiking and camping with his family in his free time, with favorite sites including the Lassen Volcanic Natural Park and the red rock country of southwestern Utah. He picked up natural photography as a hobby as well.
Glazer is survived by his wife, Eva; daughter, Judy; son, John; their spouses, Brian and Nandita; and four grandchildren.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in People
People highlights or most popular articles

Life in four dimensions: When biology outpaces the brain
Nobel laureate Eric Betzig will discuss his research on information transfer in biology from proteins to organisms at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Fasting, fat and the molecular switches that keep us alive
Nutritional biochemist and JLR AE Sander Kersten has spent decades uncovering how the body adapts to fasting. His discoveries on lipid metabolism and gene regulation reveal how our ancient survival mechanisms may hold keys to modern metabolic health.

McRose awarded Packard fellowship
She will receive $875,000 in research funding over five years.

Redefining excellence to drive equity and innovation
Donita Brady will receive the ASBMB Ruth Kirschstein Award for Maximizing Access in Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

ASBMB names 2026 fellows
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology announced that it has named 16 members as 2026 fellows of the society.

ASBMB members receive ASM awards
Jennifer Doudna, Michael Ibba and Kim Orth were recognized by the American Society for Microbiology for their achievements in leadership, education and research.