From the journals: JLR
Enzymes as a therapeutic target for liver disease. The role of AMPK in chronic liver disease. Zebra fish as a model for retinal dysfunction. Read about papers on these topics that have been recently published in the Journal of Lipid Research.
Enzymes as a therapeutic target for liver disease
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, is a leading cause of liver disease. It causes liver inflammation, fat accumulation and cell damage, and can lead to more severe conditions, such as cirrhosis and liver cancer if left untreated. Despite its severity, there are currently no Federal Drug Administration–approved drugs to treat NASH.
Antisense oligonucleotide therapy, or ASO therapy, prevents RNA synthesis by directly blocking it or cleaving the complementary strand. Researchers hypothesized that this therapeutic approach might help them target a common mutation of the HSD17B13 gene, which encodes a lipid droplet–associated enzyme called hydroxysteroid 17-beta dehydrogenase 13. Others previously showed that decreasing this protein’s abundance can lessen NASH severity.
Yanling Ma and colleagues at Bristol-Meyers Squibb Company recently published their work in the Journal of Lipid Research. They treated mice fed a high-fat diet with Hsd17b13 ASO to knock out the gene HSD17B13. Using this model in conjunction with in vitro studies on primary hepatocytes, the authors found that Hsd17b13 ASO inhibits the target gene expression and lessens NASH severity.
They also noted that, despite a reduction of steatosis in mice, Hsd17b13 ASO did not impact the severity of liver fibrosis in the mice. In the mice, there was no difference in fibrosis-related genes including Col1a1, Col1a2, Etfg and Tgfb or inflammatory related genes such as Cxcl10, Tnfa and Il1b. This study highlights that further experimentation is needed to elucidate the mechanisms behind Hsd17b13 ASO both in cells and mice.
Role of AMPK in chronic liver disease
The enzyme AMP-activated protein kinase, or AMPK, drives increased catabolism when energy levels are low. Julia R.C. Nunes and team at the University of Ottawa proposed a link between AMPK metabolic programming in myeloid cells and chronic liver disease progression in a recent Journal of Lipid Research article. The authors suggested that macrophage inflammation and activation may be influenced by AMPK to affect disease progression.
In addition, the researchers wanted to understand how metformin, a common therapy for diabetes and activator of AMPK, may be protective against liver disease. They used a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH, which specifically eliminated AMPK in monocytes and macrophages, and compared them to mice on a control and NASH-inducing diet to evaluate the efficacy of metformin treatment.
They showed that deletion of AMPK in the macrophages alone did not alter markers of steatosis, but significantly worsened indicators of fibrosis, suggesting that basal levels of myeloid AMPK signaling are critical for restraining NASH progression. However, subsequent treatment with metformin improved signs of NASH, such as liver fibrosis and steatosis in all mice. The authors concluded that deletion of AMPK did not impact markers of inflammation in the liver, suggesting that AMPK plays an integral role in driving liver fibrosis, but metformin likely acts independently of this mechanism. The team proposed that testing metformin against varying doses of AMPK activators in cell-specific models may further elucidate the cell type and signaling mechanism responsible for NASH progression.
Zebra fish as a model for retinal dysfunction
Very long-chain polyunsaturated fats, or VLC-PUFAs, may help maintain retinal structure integrity and membrane fluidity. Elovl4b is an enzyme crucial for the rate-limiting and elongation steps in VLC-PUFA synthesis. Mutations in Elovl4b often lead to protein mislocalization, as well as aggregation in the cytoplasm, both of which cause photoreceptors death. In humans, mutation of this gene often leads to macular degeneration. Research on ELOVL4 is difficult because knocking this gene out in mice is lethal.
Uzoamaka Nwagbo and their team of researchers at the University of Utah developed a zebra fish model using CRISPR–Cas9 to study Elovl4b. They published their work in the Journal of Lipid Research. They found that Elovl4b deletion decreased in the abundance of major lipid classes compared to their normal counterparts. The abnormal deposition of these major lipid classes disrupted visual function in larval zebra fish without affecting the general morphology of the retina, suggesting that shifts in lipid profiles may affect ocular function.
This work provides a useful model for future studies and could be used in the future to test treatments for VLC-PUFA–driven ocular disease.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
How bacteria fight back against promising antimicrobial peptide
Researchers find a mutation in E. coli that reduces its susceptibility to a potential novel antibiotic. Read more about this recent Journal of Biological Chemistry paper.
New clues reveal how cells respond to stress
Redox signaling protein may help regulate inflammasome and innate immune activation. Read more about this recent Journal of Biological Chemistry paper.
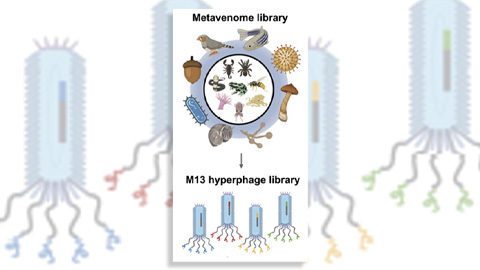
Innovative platform empowers scientists to transform venoms into therapeutics
Scientists combine phage display and a “metavenome” library to discover new drugs that bind clinically relevant human cell receptors. Read about this recent Molecular & Cellular Proteomics paper.

Meet Shannon Reilly
The JLR junior associate editor discusses the role of adipocytes in obesity at Weill Cornell Medical School.

Meet Donita Brady
Donita Brady is an associate professor of cancer biology and an associate editor of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, who studies metalloallostery in cancer.

Glyco get-together exploring health and disease
Meet the co-chairs of the 2025 ASBMB meeting on O-GlcNAcylation to be held July 10–13, 2025, in Durham, North Carolina. Learn about the latest in the field and meet families affected by diseases associated with this pathway.

