You say genome editing, I say natural mutation
For tens of thousands of years, evolution shaped tomatoes through natural mutations. Then, humans came along. For centuries, we’ve bred and cherry-picked tomatoes with our preferred traits. Today, CRISPR genome editing allows us to make new crop mutations that improve traits even further. However, individual mutations, whether natural or engineered, don’t work alone. Each operates in a sea of thousands of so-called “background” mutations. These changes have been sowed by evolution and agricultural history. And what if just one could dramatically alter the desired outcome of an engineered mutation?
Now, a plant geneticist and a computational scientist at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory have teamed up to explore just how predictable plant breeding actually is with natural and CRISPR mutations. To do so, they turned back the evolutionary clock.
CSHL Professor and HHMI investigator Zachary Lippman and Associate Professor David McCandlish wondered if different natural and engineered mutations could have similar effects on tomato size depending on the presence of two other gene mutations. Using CRISPR, they created a series of mutations in the SlCLV3 gene. (Natural mutation of this gene is known to increase fruit size.) They then combined those mutations with others in genes that work with SlCLV3.
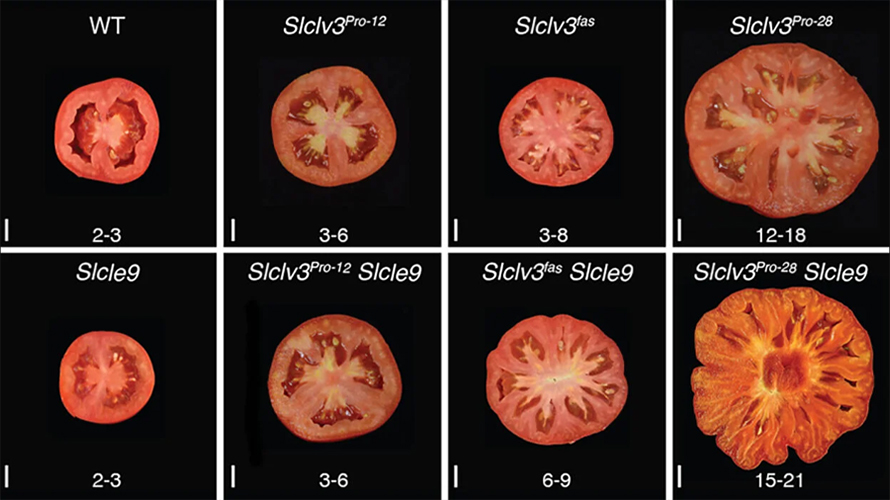

Altogether, they created 46 tomato strains with different combinations of mutations. They found the SlCLV3 mutations produced more predictable effects when certain other mutations were also present. Mutations in one gene produced predictable changes in tomato size, but mutations in another yielded random outcomes. Remarkably, the most beneficial effect involved two mutations that arose millennia ago and were central in tomato domestication.
New research by McCandlish and Lippman may help us better understand genetic predictability. But one thing’s certain. Context matters when introducing new crop mutations. Lippman explains:
“Is genome editing a way to quickly bring in consumer benefits — better flavor, nutrition? The answer is probably yes. The question is how predictable is it going to be.”
Lippman and McCandlish’s work suggests the role of background mutations demands reassessment. “The field will have to grapple with this as we start to make more highly engineered organisms,” says McCandlish. “Once you start making 10, 20 mutations, the probability of having unanticipated results may increase.”
The book of evolution has been written in all different languages, many of which we’re still learning. Plant genetics and computational biology offer two means of deciphering the text. Lippman and McCandlish hope their collaborative interpretation will help science meet the challenge. Looking ahead, it may also help humanity adapt crops to meet the ever-evolving needs of society.
This article was first published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory. Read the original.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.

Decoding how bacteria flip host’s molecular switches
Kim Orth will receive the Earl and Thressa Stadtman Distinguished Scientists Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

