From the journals: MCP
Microglia EVs as biomarkers for neuronal diseases. Automated workflow for single-cell proteomics. Circadian rhythmic protein analysis in tissues. Read about papers on these topics recently published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
Microglia EVs: Biomarkers for neuronal diseases
Microglia are vital immune cells of the central nervous system that mediate neuroinflammatory responses through the secretion of extracellular vesicles, or EVs. Although previous studies showed the significance of microglia-derived EVs in neurological diseases with unique proteomics profiles, scientists still do not understand the impact of different microglial activation states on neuroinflammation.
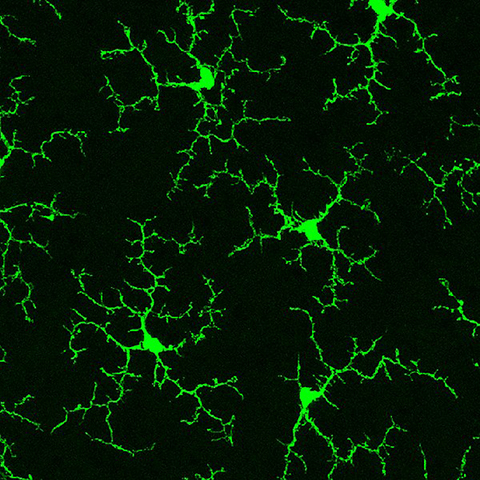
In a recent article published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Juliet Santiago and a team of researchers at Emory University describe how they examined a mouse-derived microglial cell line, BV2, and BV2-derived EVs at different conditions. They used LPS to polarize BV2 cells to a proinflammatory state and IL-10 and TGFB to polarize BV2 cells to protective and homeostatic states, respectively. Using size exclusion chromatography, the authors purified the EVs released by the BV2 microglia. In addition, they used label-free quantitative mass spectrometry and RNA sequencing to characterize and analyze the proteomic and transcriptomic profiles of microglia-derived EVs.
The authors identified both classic and novel EV proteins, including cytoskeletal proteins, heat shock proteins, integrins and tetraspanins along with mRNAs and microRNAs associated with distinct microglial activation states. LPS treatment of BV2 microglia most dramatically altered both the transcriptomic and proteomic profiles of the microglia-derived EVs compared to other treatments. Specifically, LPS increased mRNA transport to the EVs.
These findings suggest that BV2 microglial polarization affects EV cargo, potentially contributing to inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, EV cargo may serve as biomarkers and pave the way for studying the mechanisms by which microglia-derived EV cargo contributes to disease progression.
Automated workflow for single-cell proteomics
Single-cell proteomics, or SCP, has advanced the study of biological processes at the individual cell level. Protein analysis of single cells can uncover cellular identity and phenotypes through liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, or LC-MS/MS. However, problems with analysis throughput and peptide loss remain despite advancements in specialized instrumentation.
In a recent article in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Claudia Ctortecka and David Hartlmayr from the Research Institute of Molecular Pathology at the Vienna BioCenter, the Broad Institute and an international team presented an automated nanowell-array platform for multiplexed SCP samples. Using a platform called proteoCHIP, they efficiently processed and analyzed up to 576 single cells per experiment.
By using a single-cell isolation and picoliter dispenser, cellenONE, the authors reduced the sample volume and eliminated manual sample handling. With a novel nanowell-array technology, they used nanowells to hold low-input samples in combination with a labeling technique, called tandem mass tags, which are markers to identify peptides. In addition, the workflow also used field-asymmetric ion mobility mass spectrometry to analyze the peptides. This novel technology enables protein quantification in rare single cells and, overall, increases the number of proteins researchers can characterize.
Circadian rhythmic protein analysis in tissues
Circadian rhythm follows a 24-hour oscillation pattern in mammals that is regulated by core clock target genes, such as Per1 and Per2. In addition, circadian rhythm regulates nucleotide excision repair, or NER, a DNA repair mechanism. The absence of NER can increase cancer risk and accelerate aging. While researchers are studying levels of circadian proteins individually in tissues and at the transcriptome level, they do not yet know how Per1 and Per2 contribute to NER.
Liujia Qian Yue Gu, Qiaocheng Zhai and Zhangzhi Xue and their research team based in China published a study in the journal of Molecular & Cellular Proteomics tracking rhythmic proteins using tandem mass tag–based proteomics in mice lacking Per1 and Per2. They quantified dynamic alterations in over 11,000 proteins across eight tissues. The absence of these proteins led to temporal dissonance of the circadian proteome and disrupted behaviors, including sleep, exercise and feeding. In addition, the authors showed that lack of Per1 and Per2 partially inhibited NER and cell proliferation.
Future studies will explore the roles of circadian proteins in chronochemotherapy, a cancer treatment method that involves administering chemotherapy when the body is least susceptible to its harmful effects and when cancer cells are most vulnerable.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Meet Donita Brady
Donita Brady is an associate professor of cancer biology and an associate editor of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, who studies metalloallostery in cancer.

Glyco get-together exploring health and disease
Meet the co-chairs of the 2025 ASBMB meeting on O-GlcNAcylation to be held July 10–13, 2025, in Durham, North Carolina. Learn about the latest in the field and meet families affected by diseases associated with this pathway.
Targeting toxins to treat whooping cough
Scientists find that liver protein inhibits of pertussis toxin, offering a potential new treatment for bacterial respiratory disease. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Elusive zebrafish enzyme in lipid secretion
Scientists discover that triacylglycerol synthesis enzyme drives lipoproteins secretion rather than lipid droplet storage. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Biological Chemistry.

Scientists identify pan-cancer biomarkers
Researchers analyze protein and RNA data across 13 cancer types to find similarities that could improve cancer staging, prognosis and treatment strategies. Read about this recent article published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
New mass spectrometry tool accurately identifies bacteria
Scientists develop a software tool to categorize microbe species and antibiotic resistance markers to aid clinical and environmental research. Read about this recent article published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.

