Studying protein–lipid interactions
Almost every signaling event in cells has a component that includes the recruitment of signaling proteins to lipid membranes. The proper recruitment, assembly and activation of these enzymes is integral to how cells live, divide and move. In recent years, we have seen a sea change in our ability to study lipid signaling systems, primarily through major advancements in cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography. This allows for molecular analysis of how integral membrane proteins are regulated and provides insight into novel strategies to treat myriad human diseases including cancer and metabolic syndrome.
One remaining challenge in characterizing lipid signaling at the molecular level is the study of peripheral membrane proteins and how they interact with lipids. These proteins (enzymes) reside in a cytosolic location in the absence of signals and, upon activation by various stimuli, are recruited to specific membrane surfaces to carry out their function. Misregulation of how lipid signaling enzymes are recruited to membranes is implicated directly in cancer and immune deficiencies. Researchers have used a variety of techniques to study this problem, including nuclear magnetic resonance, molecular dynamic simulations and other biophysical approaches (surface plasmon resonance, protein-lipid Förster resonance energy transfer, single molecular total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy and so on). All these approaches have distinct advantages and disadvantages, but together they provide unique insight into how proteins interact with and are recruited to specific membrane surfaces.
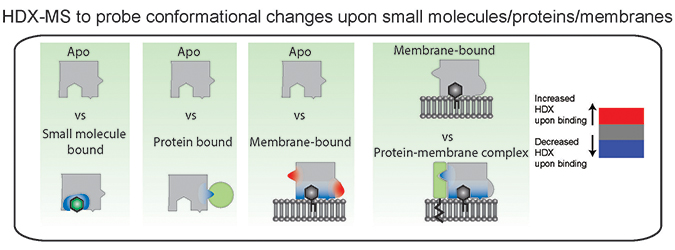 Hydrogen–deuterium exchange is a useful technique to probe conformational changes that occur upon small molecule, protein, and membrane interactions. Colors in the figure represent regions that undergo conformational changes in the bound state. Experiments require a comparison to an apo unbound state, with all conformational changes representing the sum total of both direct and allosteric conformational changes that occur upon binding. Courtesy of John BurkeA new tool used to study how proteins interact with lipid membranes is hydrogen–deuterium exchange mass spectrometry, or HDX-MS. This approach is conceptually simple, as hydrogens, specifically amide hydrogens, within proteins exchange with solvent, and this exchange is dependent primarily on the stability of protein secondary structure. This occurs because amide hydrogens are protected from exchange with solvent by their participation in hydrogen bonds in alpha helices and beta sheets. When a protein is shifted into a different chemical environment, in this case bound to a membrane, any regions with differences in protein conformation will experience a change in amide exchange. The exchange of individual amides is localized through digesting the protein and measuring the mass of fragments using a mass spectrometer. This can be compared across different conditions (apo, membrane bound, bound to specific lipids, disease-linked mutants and so on), revealing unique conformational changes for each.
Hydrogen–deuterium exchange is a useful technique to probe conformational changes that occur upon small molecule, protein, and membrane interactions. Colors in the figure represent regions that undergo conformational changes in the bound state. Experiments require a comparison to an apo unbound state, with all conformational changes representing the sum total of both direct and allosteric conformational changes that occur upon binding. Courtesy of John BurkeA new tool used to study how proteins interact with lipid membranes is hydrogen–deuterium exchange mass spectrometry, or HDX-MS. This approach is conceptually simple, as hydrogens, specifically amide hydrogens, within proteins exchange with solvent, and this exchange is dependent primarily on the stability of protein secondary structure. This occurs because amide hydrogens are protected from exchange with solvent by their participation in hydrogen bonds in alpha helices and beta sheets. When a protein is shifted into a different chemical environment, in this case bound to a membrane, any regions with differences in protein conformation will experience a change in amide exchange. The exchange of individual amides is localized through digesting the protein and measuring the mass of fragments using a mass spectrometer. This can be compared across different conditions (apo, membrane bound, bound to specific lipids, disease-linked mutants and so on), revealing unique conformational changes for each.
The technique measures exchange rates throughout the entire protein, and conformational changes due to either direct membrane interactions or allosteric conformational changes will be observed. This is particularly useful in the study of large, complicated multidomain signaling complexes with experiments on the phosphoinositide 3-kinases revealing how previously undescribed disease-causing mutations mediate altered lipid signaling through unexpected allosteric conformational changes.
Due to great advances in the last decade in the instrumentation and software for HDX-MS experiments, studies examining protein complexes larger than 500 kDa on membrane surfaces are now commonplace. This provides the larger lipid signaling community with novel opportunities to more carefully define how peripheral membrane signaling complexes are regulated.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

The data that did not fit
Brent Stockwell’s perseverance and work on the small molecule erastin led to the identification of ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death with implications for cancer, neurodegeneration and infection.

Building a career in nutrition across continents
Driven by past women in science, Kazi Sarjana Safain left Bangladesh and pursued a scientific career in the U.S.

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

