JBC: A shadowy organizational hub in cells
On a cellular level, we are all hanging on by delicate threads. All cells are crisscrossed by a network of strands called microtubules, which act as railroad tracks that move cargo around the cell, as winch cables that separate chromosomes during cell division and as scaffolding components that give a cell its shape.
Because of its essential role in the cell cycle, microtubule assembly is the target of essential anti-cancer chemotherapies (paclitaxel, for example), which stop out-of-control cell division by destabilizing microtubules. Now, researchers have shed light on the role that a large, enigmatic protein plays in assembling microtubules, paving the way for better treatments. The results of the research were published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
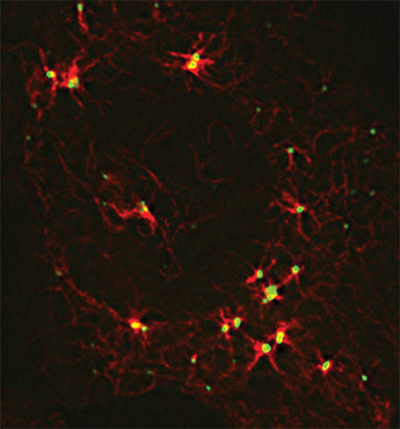 A large protein coordinates cellular components required for microtubule assembly.Courtesy of James Goldenring, Vanderbilt University
A large protein coordinates cellular components required for microtubule assembly.Courtesy of James Goldenring, Vanderbilt University
In 1999, James Goldenring’s research team at Vanderbilt University showed that protein kinase A-anchoring protein 350, or AKAP350, is a component of the centrosome, a center of microtubule organization in human cells. The team later showed that microtubules did not form efficiently without AKAP350. But the way in which AKAP350 regulated microtubule formation was difficult to understand, largely because of the technical challenges posed by AKAP350’s heft.
“Since this protein is so huge, it’s very difficult to study it,” said Elena Kolobova, the research scientist in Goldenring’s laboratory who led the new study. “A few years ago, we finally came to develop synthetic constructs of (AKAP350), which allowed us to go to the next level of evaluation and function.”
Using a combination of detailed biochemical analyses and super-resolution microscopy, the team finally was able to gain some understanding of the complex roles that AKAP350 plays in regulating microtubules in cells. AKAP350 formed a physical bridge spanning components of the centrosome. And AKAP350 appeared to recruit multiple proteins involved in building microtubules, coordinating their function in one spot.
“I like to call this thing Deep Space Nine. Everybody comes to hang out at AKAP350,” Goldenring said. “I think we’ve only scratched the surface of the structural organization that this protein is probably providing.”
Mutations in AKAP350 have been associated with cardiac arrhythmias, so it will be of interest to see whether the protein’s role in microtubule assembly contributes to proper heart function as well.
“I think (AKAP350) is a fundamental regulator of cell function,” Goldenring said. “So we need to know a lot more about this protein before we can even begin looking at what it might mean for disease.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

E-cigarettes drive irreversible lung damage via free radicals
E-cigarettes are often thought to be safer because they lack many of the carcinogens found in tobacco cigarettes. However, scientists recently found that exposure to e-cigarette vapor can cause severe, irreversible lung damage.

Using DNA barcodes to capture local biodiversity
Undergraduate at the University of California, Santa Barbara, leads citizen science initiative to engage the public in DNA barcoding to catalog local biodiversity, fostering community involvement in science.

Targeting Toxoplasma parasites and their protein accomplices
Researchers identify that a Toxoplasma gondii enzyme drives parasite's survival. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Scavenger protein receptor aids the transport of lipoproteins
Scientists elucidated how two major splice variants of scavenger receptors affect cellular localization in endothelial cells. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Fat cells are a culprit in osteoporosis
Scientists reveal that lipid transfer from bone marrow adipocytes to osteoblasts impairs bone formation by downregulating osteogenic proteins and inducing ferroptosis. Read more about this recent study from the Journal of Lipid Research.

Unraveling oncogenesis: What makes cancer tick?
Learn about the ASBMB 2025 symposium on oncogenic hubs: chromatin regulatory and transcriptional complexes in cancer.

.jpg?lang=en-US&width=300&height=300&ext=.jpg)