From the journals: MCP
We offer a selection of papers on a variety of topics recently published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics.
CEP5 helps plants tolerate droughts
Environmental stresses, such as drought, affect plant growth, development and reproduction. In a recent paper published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Stephanie Smith of the University of Nottingham in the UK and Shanshuo Zhu of VIB/University of Ghent in Belgium, together with an international team reported a previously unknown role for the CEP5 peptide in osmotic and drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. They propose that the peptide stabilizes auxin transcriptional repressors and fine-tunes the level of auxin signaling.
CEP5 previously was shown to play a role in shoot and root growth. To better understand activity downstream of the peptide, the researchers quantified differences between the proteomes and phosphoproteomes of normal shoots and those of shoots overexpressing CEP5. Based on gene ontology annotations, they write that 30% of the proteins that were upregulated or downregulated were involved in “response to stress” while 17% were involved in “response to abiotic stimulus.”
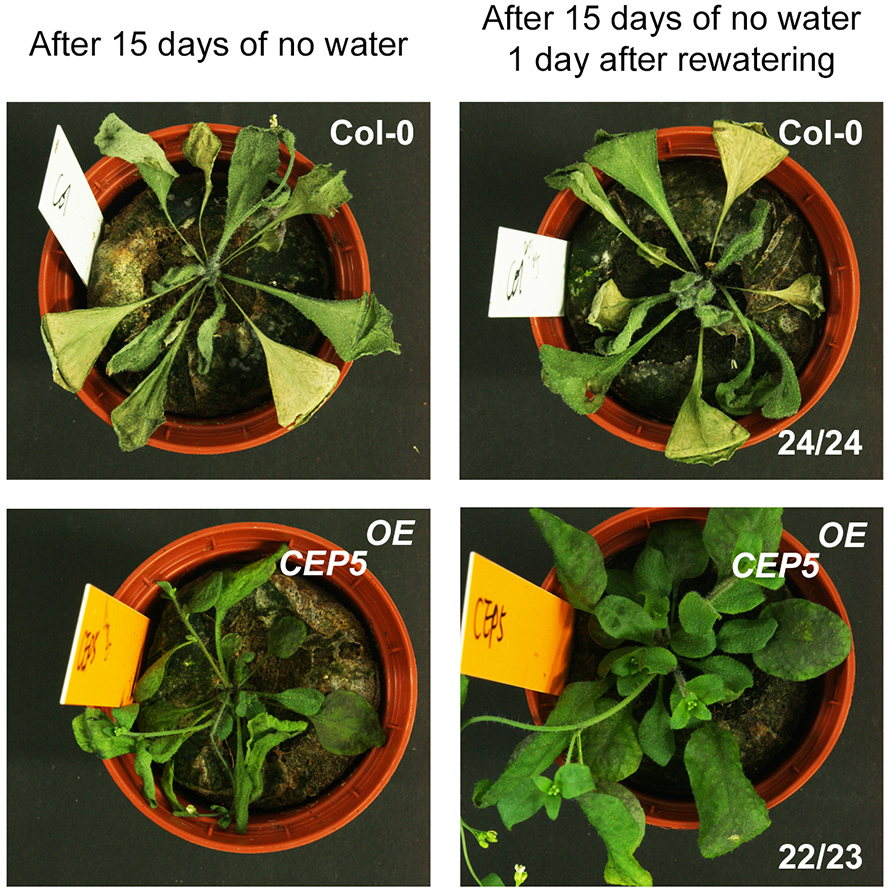
Consistent with these findings, CEP5-overexpressing plants withstood drought stress tolerance tests better than normal plants. After 15 days without water, normal plants were pale and wilted, but nearly all the overexpressing plants still had green leaves. The researchers saw similar tolerance to osmotic stress. They observed elevated expression of stress-related transcription factors in CEP5-overexpressing plants even under unstressed conditions; they propose that this readies plants for future stress conditions.
Auxin is a plant hormone involved in growth and developmental processes. Auxin-responsive markers had reduced activity in plants overexpressing CEP5. Additional CEP5 also led to quick stabilization or accumulation of transcriptional repressors of auxin signaling. Seedlings overexpressing the peptide were more sensitive to chemical or genetic interference of proteasome activity than normal seedlings.
These results indicate that CEP5 affects auxin-mediated processes, including drought and osmotic stress tolerance. Future work is needed to identify all the proteins involved, but the results support a new model for regulating auxin transcription repressors.
Identifying acetylation sites in a coronavirus
Like the virus that causes COVID-19, MERS-CoV is a coronavirus that can cause severe respiratory illness. A better understanding of how host cells respond to MERS-CoV infection could help prevent a future pandemic.
Some other viruses require protein acetylation for viral replication; in a recent paper published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Lin Zhu of Hong Kong Baptist University and a team of Hong Kong researchers explored whether MERS-CoV proteins also are acetylated by host factors.
After obtaining viral proteins from infected cells, the researchers enriched for peptides with acetylated lysine residues. All the acetylated peptides corresponded to pp1ab, a polyprotein that forms 15 different proteins involved in MERS-CoV replication. Bioinformatic analysis suggested that proteins in the SIRT1, HDAC and TIP60 families could be upstream regulators of these acetylation sites. Experiments are needed to confirm the actual role of the acetylated proteins during viral replication, but the study’s findings hint at possible therapeutic targets to explore.
Deamidation is rife in the immunopeptidome
T cells target infected and damaged cells by recognizing peptides presented on cell surfaces by human leukocyte antigen. Post-translational modification of these peptides expands the variety of possible signals displayed by cells. But few systematic studies have explored modifications across the entire immunopeptidome.
In a recent paper published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, Shutao Mei of Monash University and a team of Australian researchers found that 2.5% to 7% of associated peptides are deamidated, with the amide group removed from asparagine and glutamine residues.
The researchers analyzed the amino acids flanking the deamidated residues to identify possible motifs. They found a pattern for asparagine: a preference for threonine or serine two positions following the affected residue. This motif, NX(S/T), is canonical for N-linked glycosylation.
The researchers tested a possible role of peptide:N-glycanase, or PNGase; this enzyme removes N-linked glycans from misfolded glycoproteins and is known to deamidate asparagine. In the presence of a PNGase inhibitor, the immunopeptidome contained significantly fewer NX(S/T)-containing peptides. The researchers propose asparagine deamidation as a means for the immune system to identify cells with perturbed N-glycosylation for elimination.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.

