Eye-opening origin story
Humans and other organisms with backbones come equipped with an evolutionary marvel: eyes that function like cameras to provide a finely tuned visual system. Due to its complexity, Charles Darwin described the eye as one of the greatest potential challenges to his theory of natural selection through incremental evolutionary steps.
A notable difference between vertebrate and invertebrate vision is rooted in a unique protein responsible for the specialization of cells that are critical for vision. Mutations in the protein, called the interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein, or IRBP, have been known to cause a variety of diseases such as retinitis pigmentosa, but its evolutionary origin has remained elusive with no obvious genetic precursor.
Scientists in the University of California San Diego School of Biological Sciences, publishing in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, have now traced the 500-million-year-old origin of vertebrate IRBP to a bacterial source. Their discovery, using phylogenetic reconstruction methods, was made possible because of the growing number of fully detailed genomes now available. Their analysis of more than 900 genomes across the tree of life revealed that the IRBP integration in vertebrate eyes was not the result of traditional vertical gene transfer, in which an evolutionary advancement is adapted, or “tinkered with” using available genetic material. Rather, the IRBP was acquired, duplicated and integrated through horizontal gene transfer from foreign bacterial genes.
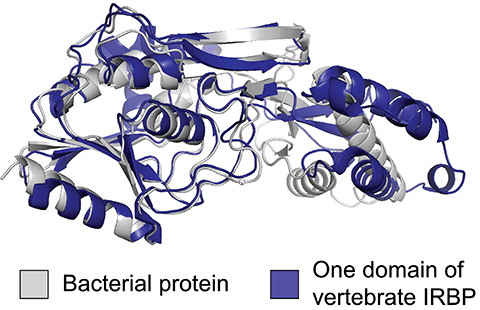
“It’s a massive shift because this is an entirely new piece of genetic material that’s been introduced from bacteria,” said Associate Professor Matt Daugherty, the paper’s senior author. Former UC San Diego undergraduate student Chinmay Kalluraya led the study, and UC San Diego graduate students Alexander Weitzel and Brian Tsu contributed computational expertise. “This study shows that a major innovation that distinguishes vertebrate eyes from all the rest of the eyes out there wasn’t done by molecular tinkering but rather a big leap of genetic innovation.”
Once the key gene that eventually became IRBP was acquired from bacteria, a new door opened in vertebrates that allowed retinoids, molecules in the eye that directly sense light, to be shuttled between cell types to efficiently recycle it for further light sensing. This separation of photoreception, or light sensing, and retinoid recycling provides unique functionality to vertebrates and the way they can see.
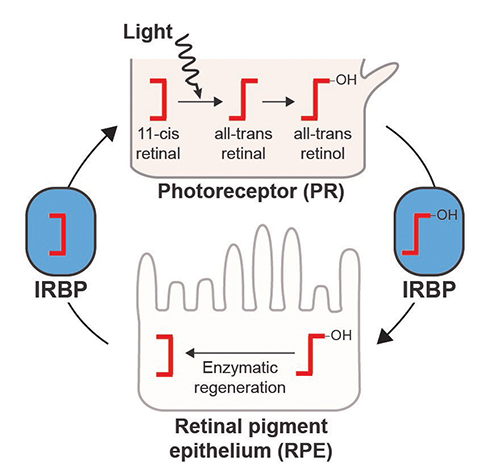
“In order to see in different wavelengths, there needs to be enough light around and that’s one of the arguments for why we can see in the dark really well—we have this enzymatic recycling system that many invertebrates don’t seem to have,” said Daugherty, a researcher in the molecular biology department. “Eyes are diverse and complicated, and we’ve gone down this path because of this system.”
With more genomes from more organisms becoming available, the researchers believe that other critical functions and systems will similarly trace their roots to bacteria.
“This reshapes the way that we think about evolution and the way we think about complex structures that seem like they’ve emerged out of nowhere,” said Daugherty.
This article first appeared in UC San Diego Today. Read the original.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Redefining lipid biology from droplets to ferroptosis
James Olzmann will receive the ASBMB Avanti Award in Lipids at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Women’s health cannot leave rare diseases behind
A physician living with lymphangioleiomyomatosis and a basic scientist explain why patient-driven, trial-ready research is essential to turning momentum into meaningful progress.

Life in four dimensions: When biology outpaces the brain
Nobel laureate Eric Betzig will discuss his research on information transfer in biology from proteins to organisms at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Fasting, fat and the molecular switches that keep us alive
Nutritional biochemist and JLR AE Sander Kersten has spent decades uncovering how the body adapts to fasting. His discoveries on lipid metabolism and gene regulation reveal how our ancient survival mechanisms may hold keys to modern metabolic health.

Redefining excellence to drive equity and innovation
Donita Brady will receive the ASBMB Ruth Kirschstein Award for Maximizing Access in Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Mining microbes for rare earth solutions
Joseph Cotruvo, Jr., will receive the ASBMB Mildred Cohn Young Investigator Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

