New study discovers tiny target on RNA to short-circuit inflammation
University of California, Santa Cruz researchers have discovered a peptide in human RNA that regulates inflammation and may provide a new path for treating diseases such as arthritis and lupus. The team used a screening process based on the powerful gene-editing tool CRISPR to shed light on one of the biggest mysteries about our RNA–the molecule responsible for carrying out genetic information contained in our DNA.
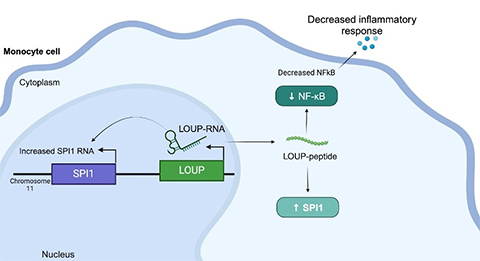
This peptide originates from within a long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) called LOUP. According to the researchers, the human genome encodes over 20,000 lncRNAs, making it the largest group of genes produced from the genome. But despite this abundance, scientists know little about why lncRNAs exist or what they do. This is why lncRNA is sometimes referred to as the "dark matter of the genome."
The study, published May 23 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), is one of the very few in the existing literature to chip away at the mysteries of lncRNA. It also presents a new strategy for conducting high-throughput screening to rapidly identify functional lncRNAs in immune cells. The pooled-screen approach allows researchers to target thousands of genes in a single experiment, which is a much more efficient way to study uncharacterized portions of the genome than traditional experiments which focus on one gene at a time.
The research was led by immunologist Susan Carpenter, a professor and Sinsheimer Chair of UC Santa Cruz's Molecular, Cell, and Developmental Biology Department. She studies the molecular mechanisms involved in protection against infection. Specifically, she focuses on the processes that lead to inflammation to determine the role that lncRNAs play in these pathways.
"Inflammation is a central feature of just about every disease," she said. "In this study, my lab focused on trying to determine which lncRNA genes are involved in regulating inflammation."
This meant studying lncRNAs in a type of white blood cell known as a monocyte. They used a modification of the CRISPR/Cas9 technology, called CRISPR inhibition (CRISPRi), to repress gene transcription and find out which of a monocyte's lncRNAs play a role in whether it differentiates into a macrophage—another type of white blood cell that's critical to a well-functioning immune response.
In addition, the researchers used CRISPRi to screen macrophage lncRNA for involvement in inflammation. Unexpectedly, they located a region that is multifunctional and can work as an RNA as well as containing an undiscovered peptide that regulates inflammation.
Understanding that this specific peptide regulates inflammation gives drugmakers a target to block the molecular interaction behind that response in order to suppress it, Carpenter said. "In an ideal world, you would design a small molecule to disrupt that specific interaction, instead of, say, targeting a protein that might be expressed throughout the body," she explained. "We're still a long way from targeting these pathways with that level of precision, but that’s definitely the goal. There's a lot of interest in RNA therapeutics right now."
This article is republished from the University of California, Santa Cruz Newscenter. Read the original here.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Building better tools to decipher the lipidome
Chemical engineer–turned–biophysicist Matthew Mitsche uses curiosity, coding and creativity to tackle lipid biology, uncovering PNPLA3’s role in fatty liver disease and advancing mass spectrometry tools for studying complex lipid systems.

Redefining lipid biology from droplets to ferroptosis
James Olzmann will receive the ASBMB Avanti Award in Lipids at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Women’s health cannot leave rare diseases behind
A physician living with lymphangioleiomyomatosis and a basic scientist explain why patient-driven, trial-ready research is essential to turning momentum into meaningful progress.

Life in four dimensions: When biology outpaces the brain
Nobel laureate Eric Betzig will discuss his research on information transfer in biology from proteins to organisms at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Fasting, fat and the molecular switches that keep us alive
Nutritional biochemist and JLR AE Sander Kersten has spent decades uncovering how the body adapts to fasting. His discoveries on lipid metabolism and gene regulation reveal how our ancient survival mechanisms may hold keys to modern metabolic health.

