Saving injera: Lessons from a teff grain's drought-tolerant cousin
Eragrostis nindensis is known as a resurrection plant: Even after a drought that would kill other grasses, and even if it has shriveled to a dead brown husk, it can rebound and sprout new green shoots when water becomes available.
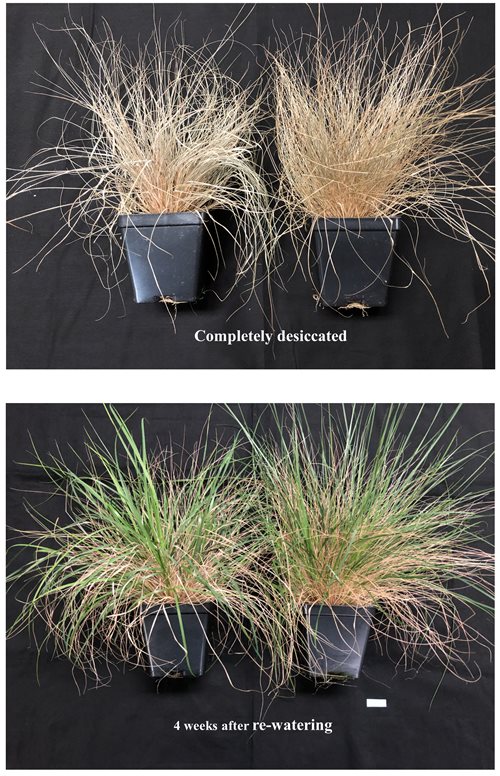

“It was completely desiccated. Dead,” Shivaiah said. “Nobody thought it would come back. But I started watering and within four weeks … it came back to life.”
Like other researchers in Peter Lundquist’s lab, Shivaiah is interested in how plastoglobules, lipid droplets found in the chloroplast, mediate stress responses. He found that as nindensis stems dry, their plastoglobules increase in size. Nindensis is known to destroy its chlorophyll while drying out, to prevent photo-oxidation. Using lipidomics, Shivaiah observed that crash in chlorophyll level and an increase in smaller lipids and sugars, which he thinks are breakdown products. He suspects that some lipids are converted into sucrose, to stabilize proteins as drier conditions introduce osmotic stress. The adaptation also seems to involve reductions in the level of many plastoglobule proteins.
The findings are preliminary, Shivaiah said. After replicating them to solidify his conclusions about how the plastoglobule changes, he hopes to investigate what differentiates teff plastoglobules from those of E. nindensis.
“Teff is dessication-sensitive. It can tolerate water scarcity for a while, but not as long as E. nindensis,” he said. “Can we do genetic modification to the teff plant to make it as desiccation-tolerant as the nindensis plant?”
You can see Shivaiah's poster presentation here, as part of the Lipids and Membranes poster session, or join a discussion on Tuesday, April 27 at 3:15 p.m. EDT.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

ASBMB announces 2026 JBC/Tabor awardees
The seven awardees are first authors of outstanding papers published in 2025 in the Journal of Biological Chemistry.
Missing lipid shrinks heart and lowers exercise capacity
Researchers uncovered the essential role of PLAAT1 in maintaining heart cardiolipin, mitochondrial function and energy metabolism, linking this enzyme to exercise capacity and potential cardiovascular disease pathways.

Decoding how bacteria flip host’s molecular switches
Kim Orth will receive the Earl and Thressa Stadtman Distinguished Scientists Award at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

