PI-PLC β1 in differentiation and disease
Evidence from several laboratories has highlighted the presence of autonomous nuclear inositol lipid metabolism. The evidence suggests that lipid molecules are important components of signaling pathways operating within the nucleus. The findings are important, given the fact that nuclear signaling activity controls cell growth and differentiation.
 Inositide-specific phospholipase C plays a role in MDS and a form of muscular dystrophy.IMAGE PROVIDED BY LUCIO COCCO
Inositide-specific phospholipase C plays a role in MDS and a form of muscular dystrophy.IMAGE PROVIDED BY LUCIO COCCO
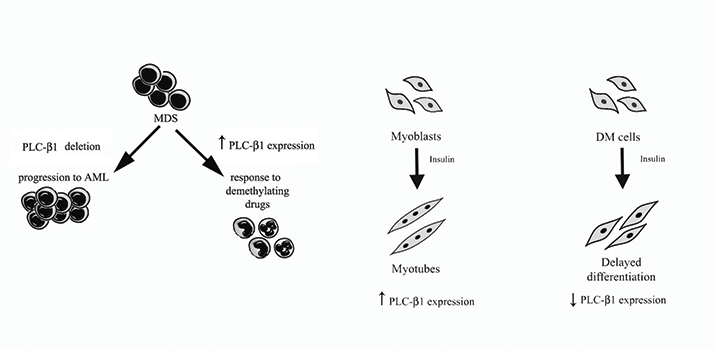
Among the nuclear enzymes involved in this system, inositide-specific phospholipase C, or PI-PLC, β1 is one of the most extensively studied enzymes. Besides the studies on its signaling activity, clinically oriented studies have shown that a mono-allelic deletion of the PI-PLCβ1 gene is associated with the evolution of myelodysplastic syndromes, or MDS, into acute myeloid leukemia. Studies also have showed that increased PI-PLCβ1 gene expression, due to reduced methylation and reactivation of its promoter, associates with responsiveness to demethylating agents, such as azacitidine, in MDS. Extensive clinical and molecular evaluation have aimed to establish a predictive role of increased PI-PLCβ1 gene expression during the first three cycles of treatment with the demethylating drug azacitidine. The data obtained hint at PI-PLCβ1 expression as a useful tool for the early identification of a subgroup of patients with a higher probability of response to azacitidine. These data suggest also a possible involvement of nuclear PI-PLCβ1 in the early stages of hemopoiesis and specifically in the control of cell-cycle progression in progenitor hemopoietic cells. Nuclear PI-PLCβ1 also is involved in myogenic differentiation.
Indeed, nuclear PI-PLCβ1 plays a crucial role in the initiation of the genetic program responsible for muscle differentiation: the enzyme activates the cyclin D3 promoter during the differentiation of myoblasts to myotubes. This indicates that PI-PLCβ1 is essential for cyclin D3 promoter activation and gene transcription through c-jun/AP1.
Myotonic dystrophy is the most prevalent form of muscular dystrophy in adults. DM type 1 and type 2 are dominantly inherited multisystem disorders. DM1 is triggered by the pathological expansion of a CTG triplet repeat in the gene coding for DMPK, the dystrophia myotonica-protein kinase. A CCTG tetranucleotide repeat expansion in the ZNF9 gene, which encodes a CCHC-type zinc-finger protein, causes DM2. Unlike in normal myotubes, the level of expression of PI-PLCβ1 in DM1 and DM2 cells already is elevated in proliferating cells. Treatment with insulin induces a dramatic decrease in the amount of PI-PLCβ1. During differentiation, cyclin D3 and myogenin are elevated in normal myotubes. When DM1 and DM2 cells are induced to differentiate, they do not show any increase in these proteins. Forced expression of PI-PLCβ1 in DM1 and DM2 cells increases the expression of differentiation markers myogenin and cyclin D3 and enhances fusion of DM myoblasts. These results highlight again that nuclear PI-PLCβ1 expression is a key player in myoblast differentiation, functioning as a positive regulator in the correction of delayed differentiation of human skeletal muscle.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Defining JNKs: Targets for drug discovery
Roger Davis will receive the Bert and Natalie Vallee Award in Biomedical Science at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Building better tools to decipher the lipidome
Chemical engineer–turned–biophysicist Matthew Mitsche uses curiosity, coding and creativity to tackle lipid biology, uncovering PNPLA3’s role in fatty liver disease and advancing mass spectrometry tools for studying complex lipid systems.

Redefining lipid biology from droplets to ferroptosis
James Olzmann will receive the ASBMB Avanti Award in Lipids at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7–10, just outside of Washington, D.C.

Women’s health cannot leave rare diseases behind
A physician living with lymphangioleiomyomatosis and a basic scientist explain why patient-driven, trial-ready research is essential to turning momentum into meaningful progress.

Life in four dimensions: When biology outpaces the brain
Nobel laureate Eric Betzig will discuss his research on information transfer in biology from proteins to organisms at the 2026 ASBMB Annual Meeting.

Fasting, fat and the molecular switches that keep us alive
Nutritional biochemist and JLR AE Sander Kersten has spent decades uncovering how the body adapts to fasting. His discoveries on lipid metabolism and gene regulation reveal how our ancient survival mechanisms may hold keys to modern metabolic health.

