MCP: Ovarian cancer’s dark signaling pathways
Ovarian cancer is considerably rarer than lung and breast cancer, but it is the seventh-most common cancer in women, and in 2012, 239,000 new cases were diagnosed worldwide. The most common subtype of ovarian cancer, high-grade serous ovarian adenocarcinoma, or HGSOC, is also the most lethal, with a five-year survival rate of less than 40 percent despite high vulnerability to early treatment with chemotherapy.
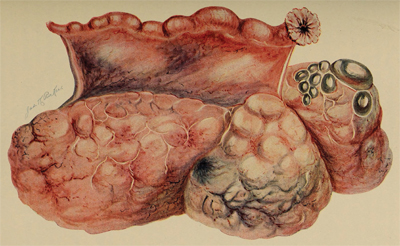 This image from the 1905 text, “The diagnosis of diseases in women” by Findley Palmer, shows an adenocarcinoma of the ovary in which, according to the caption, “(t)he ovary is enlarged to the size of a child’s head.”
This image from the 1905 text, “The diagnosis of diseases in women” by Findley Palmer, shows an adenocarcinoma of the ovary in which, according to the caption, “(t)he ovary is enlarged to the size of a child’s head.” WIKIMEDIA COMMONS/THE LIBRARY OF CONGRESS
The mortality rate is high largely because HGSOC tumors tend to shed small spheroids early and prolifically, spreading through the peritoneal fluid in the abdominal cavity to the pelvis and nearby organs. The spheroids, together with tumor-associated T cells and macrophages derived from nearby tissues and the circulation, then manufacture a microenvironment of signaling factors that promote cancer progression, immunosuppression and resistance to chemotherapies. This hostile bubble is maintained by obscure signaling mechanisms between the different cell types, and disrupting them with existing drugs may be a way to fight this notably aggressive form of cancer.
In a paper published in the journal Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, researchers at Philipps University in Marburg, Germany, have analyzed the proteome and transcriptome of the microenvironment of tumors in the abdominal fluid taken from women with HGSOC. Using state-of-the-art proteotranscriptomic techniques, the researchers have thrown light on the signaling networks and uncovered associations between factors expressed by the tumors and the likelihood of patient survival.
“We came up with a signaling map between tumor cells, macrophages and T cells,” said Rolf Müller, senior author on the paper, “and could now analyze and determine which cells secrete which mediators and on which cells these mediators act.”
Müller and colleagues previously had developed a signaling map based on the RNA, or transcriptome, expressed in tumor cells and related macrophages, but they wanted to expand their analyses to encompass the proteome and the aggregate of secreted molecules known as the secretome. Analyses of the transcriptome, proteome and secretome, Müller said, “all have their limitations on their own, (but) you can combine them to obtain something really meaningful.”
With a signaling map, Müller and colleagues were able to confirm several known signaling pathways and identify two new subgroups of macrophages, which they named B and G for their respective presence in patients with bad or good prognoses.
Müller and colleagues found that tumor spheroids and macrophages taken from patients with an estimated short survival time, based on the presence of additional factors, produced proteins that support remodeling of extracellular matrices and immunosuppression, which are both key for further cell proliferation. In contrast, macrophages taken from patients with an estimated longer survival time expressed cytokines linked to the activation and attraction of tumor-fighting effector T cells.
While clinical trials are still beyond the horizon, Müller and first author Thomas Worzfeld said they and their colleagues are interested in exploring the gamut of available pharmaceuticals that can interrupt the signaling within tumors as an alternative to disrupting extracellular communication pathways.
“There’s a drug to block almost any important intracellular signaling pathways nowadays,” Müller said, “and it would be interesting to see what the important signals are and on what intracellular signaling pathways the signals converge so that we can also block these interactions. That is something we really would like to work on in the future.”
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles

Avoiding common figure errors in manuscript submissions
The three figure issues most often flagged during JBC’s data integrity review are background signal errors, image reuse and undeclared splicing errors. Learn how to avoid these and prevent mistakes that could impede publication.

Ragweed compound thwarts aggressive bladder and breast cancers
Scientists from the University of Michigan reveal the mechanism of action of ambrosin, a compound from ragweed, selectively attacks advanced bladder and breast cancer cells in cell-based models, highlighting its potential to treat advanced tumors.

Lipid-lowering therapies could help treat IBD
Genetic evidence shows that drugs that reduce cholesterol or triglyceride levels can either raise or lower inflammatory bowel disease risk by altering gut microbes and immune signaling.

Key regulator of cholesterol protects against Alzheimer’s disease
A new study identifies oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 6 as a central controller of brain cholesterol balance, with protective effects against Alzheimer’s-related neurodegeneration.

From humble beginnings to unlocking lysosomal secrets
Monther Abu–Remaileh will receive the ASBMB’s 2026 Walter A. Shaw Young Investigator Award in Lipid Research at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

Chemistry meets biology to thwart parasites
Margaret Phillips will receive the Alice and C. C. Wang Award in Molecular Parasitology at the ASBMB Annual Meeting, March 7-10 in Washington, D.C.

