Vital fluids
You never know what you’ll turn out to have in common with your co-workers; science writer John Arnst and I bonded over selling our blood plasma.
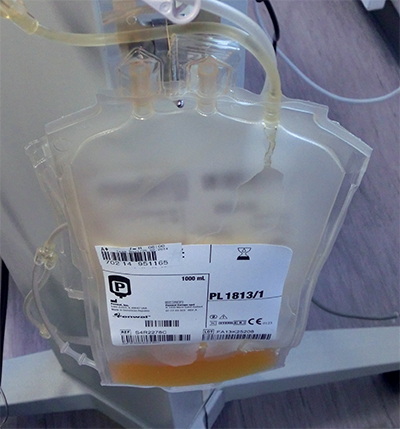
Plasma, the yellowish fluid in which blood cells and platelets are suspended, is essential for treating trauma patients and those with a number of other medical conditions. It’s needed in such large quantities that people get paid for it — though you aren’t technically being paid for the fluid; you’re being compensated for the hour or so that you spend lying in a padded lounge chair with a big needle stuck in one arm. A healthy person can donate about three cups of plasma twice a week. When I did it, my time was worth about $30 a pop.
 ANKAWÜ/Wikimedia Commons
ANKAWÜ/Wikimedia Commons
In that hour, a whirling machine separates the plasma from everything else in a process called apheresis and returns the blood cells and platelets to your arm. The machine is mostly clear plastic tubes and cylinders, so you can watch the process, which repeats about six times per donation, and monitor the slow drip of plasma into a plastic bottle. When it’s over, a pint of saline gets pushed into your arm to restore the fluid level.
Unlike blood donation, selling plasma is not an altruistic activity. It’s about the dollars on a debit card. John said he did it for about six weeks right after he graduated from college. I was an underpaid newspaper editor and single mom when I sold my plasma off and on for about a year, long enough for my arms to develop some suspicious marks and for my iron levels to dip perilously a couple of times.
While reclining in that lounge chair, I thought a fair amount about the marketing of bodily fluids, so when John mentioned Stephen Withers’ efforts to turn other blood types into O and its possible impact on the blood donation industry, all my old questions came back: Why do people get paid to donate plasma but not blood? If people give their blood for free, why does it cost so much when you get a transfusion? How do blood banks persuade enough people with the right types of blood to donate?
I was not the first person to think about this. Just Google “selling blood” and numerous articles on the topic pop up.
John writes that the blood industry is in trouble. Can it be saved by science? We don’t have an answer to that question, but our February feature story certainly lays out the issues and explains how blood (both industry and science) got where it is today. It’s a good read.
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition four times a year and the digital edition monthly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Opinions
Opinions highlights or most popular articles

Women’s health cannot leave rare diseases behind
A physician living with lymphangioleiomyomatosis and a basic scientist explain why patient-driven, trial-ready research is essential to turning momentum into meaningful progress.

Making my spicy brain work for me
Researcher Reid Blanchett reflects on her journey navigating mental health struggles through graduate school. She found a new path in bioinformatics, proving that science can be flexible, forgiving and full of second chances.

The tortoise wins: How slowing down saved my Ph.D.
Graduate student Amy Bounds reflects on how slowing down in the lab not only improved her relationship with work but also made her a more productive scientist.
How pediatric cataracts shaped my scientific journey
Undergraduate student Grace Jones shares how she transformed her childhood cataract diagnosis into a scientific purpose. She explores how biochemistry can bring a clearer vision to others, and how personal history can shape discovery.

Debugging my code and teaching with ChatGPT
AI tools like ChatGPT have changed the way an assistant professor teaches and does research. But, he asserts that real growth still comes from struggle, and educators must help students use AI wisely — as scaffolds, not shortcuts.

AI in the lab: The power of smarter questions
An assistant professor discusses AI's evolution from a buzzword to a trusted research partner. It helps streamline reviews, troubleshoot code, save time and spark ideas, but its success relies on combining AI with expertise and critical thinking.

