Progress in identifying lipid domains (rafts) in living cells
Under which conditions lipid chemical heterogeneity results in the formation of coexisting lipid domains with distinct lipid compositions and properties in living cells has been a subject of intense research for decades.
In model membrane formed from lipid mixtures, spontaneous formation of tightly packed sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich lipid domains (in the liquid-ordered state) that segregate from loosely packed domains richer in unsaturated phospholipids (in the liquid-disordered state) are detected and characterized easily.
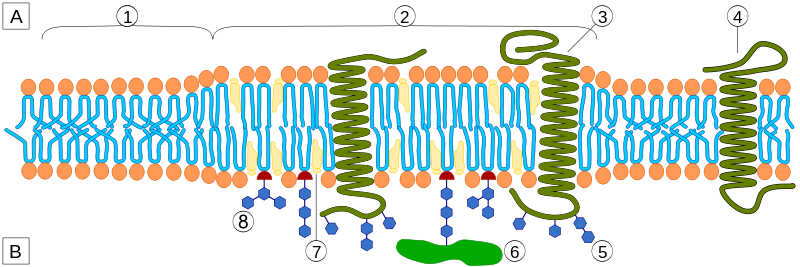
However, analogous domains in cells are very small under most conditions — at or beyond the limit of detection for most techniques. This has led to much controversy as well as much work aiming to develop new methods to identify and characterize tiny nanodomains.
Very recent progress in living cells has been encouraging on several fronts. Studies using novel fluorescently labeled lipids with affinities for liquid-ordered domains similar to those of unlabeled lipids have revealed that specific association of raft-loving lipids with raft-localizing proteins occurs in living cells (1,2). Single-particle-tracking measurements show that these interactions are lost in living cells when even minor changes in lipid or protein structure are made if these changes abolish raft-associating physical properties.
In other studies, super-resolution microscopy in B cells has found co-localization of raft markers with, and exclusion of nonraft markers from, the vicinity of clustered B-cell receptors on a size scale similar to that of the clusters (50 nanometers to 100 nanometers). This is indicative of the formation of ordered domains around the B-cell receptors. An analogous formation of nanodomains was detected around clustered cholera toxin, a molecule long known to induce the formation of ordered domains in vitro and in cells (3).
These studies extend previous work from other labs that reported lipid-domain-based molecular interactions in these systems. This is indicative of a robust underlying phenomenon.
Advances leading to an increased ability to visualize domains and manipulate their structure promise further progress. An even higher-resolution, super-resolution microscopy approach has been developed, which may allow visualization of domains that otherwise would elude direct visualization (4).
Finally, our own lab has devised a method efficiently to replace virtually the entire complement of plasma membrane outer leaflet lipids in living cells with exogenous lipids. This may allow fine-tuned control of domain formation and properties (5).
REFERENCES
1. Komura, N. et al. Nat. Chem. Biol. 12, 402 – 410 (2016).2. Kinoshita, M. et al. J. Cell. Biol. 216, 1183 – 1204 (2017).
3. Stone, M.B. et al. eLife 6, e19891 (2017).
4. Balzarotti, F. et al. Science 355, 606 – 612 (2017).
5. Li, G. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 113, 14025 – 14030 (2016).
Enjoy reading ASBMB Today?
Become a member to receive the print edition monthly and the digital edition weekly.
Learn moreGet the latest from ASBMB Today
Enter your email address, and we’ll send you a weekly email with recent articles, interviews and more.
Latest in Science
Science highlights or most popular articles
Small protein plays a big role in viral battles
Nef, an HIV accessory protein, manipulates protein expression in extracellular vesicles, leading to improved understanding of HIV-1 pathogenesis.

Genetics studies have a diversity problem that researchers struggle to fix
Researchers in South Carolina are trying to build a DNA database to better understand how genetics affects health risks. But they’re struggling to recruit enough Black participants.
Scientists identify new function of learning and memory gene common to all mammalian brain cells
Findings in mice may steer search for therapies to treat brain developmental disorders in children with SYNGAP1 gene mutations.
From the journals: JBC
Biased agonism of an immune receptor. A profile of missense mutations. Cartilage affects tissue aging. Read about these recent papers.
Cows offer clues to treat human infertility
Decoding the bovine reproductive cycle may help increase the success of human IVF treatments.
Immune cells can adapt to invading pathogens
A team of bioengineers studies how T cells decide whether to fight now or prepare for the next battle.

